Pytorch 手册
【2024-3-28】一文总结深度学习框架-Pytorch
Pytorch总览
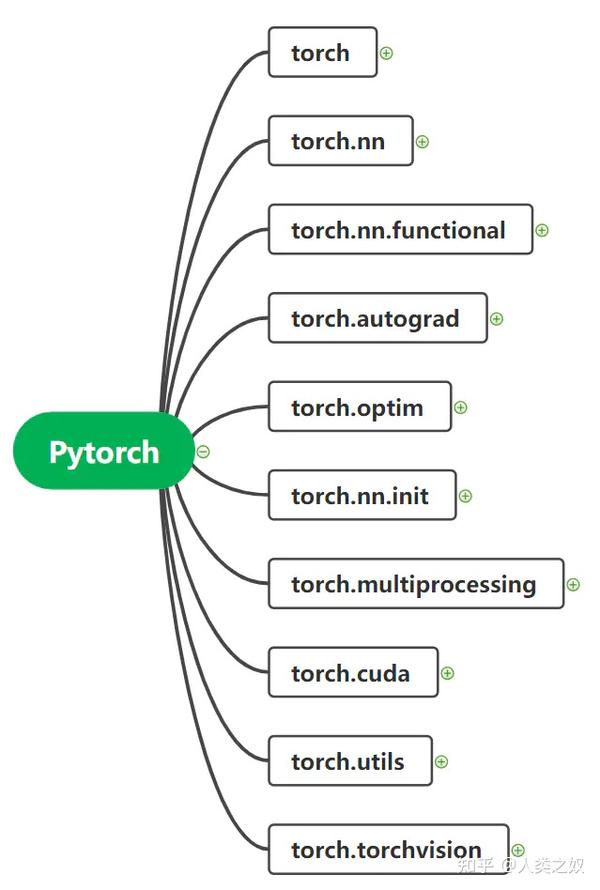
3 Pytorch详解
3.1 torch
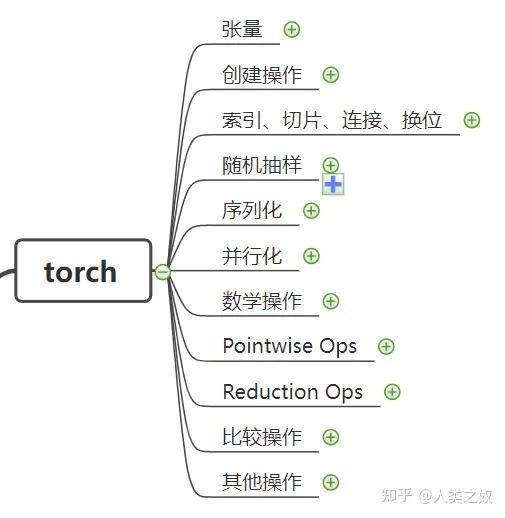
张量
| 函数功能 | |
|---|---|
| torch.is_tensor(obj) | 判断obj是否为tensor数据类型 |
| torch.is_storage(obj) | 判断obj是否为storage类型 |
| torch.set_default_tensor_type(type) | 设置默认的tensor数据类型 |
| torch.set_printoptions(precision=None,threshold=None,linewidth=None,profile=None) | 设置打印格式c |
创建操作
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.eye(n,m=None,out=None) | 创建主对角矩阵 |
| torch.zeros(*sizes,out=None) | 创建全0张量 |
| torch.ones(*sizes,out=None) | 创建全1张量 |
| torch.rand(*sizes,out=None) | 创建位于0-1的均匀分布的张量 |
| torch.randn(*sizes,out=None) | 从标准正态分布中抽取数据创建张量 |
| torch.arange(start,end,step=1,out=None) | 创建一维张量 |
| torch.linspace(start,end,steps=100,out=None) | 创建含steps个元素的一维张量 |
| torch.logspace(start,end,steps=100,out=None) | 创建位于10^start-10^end内的一维张量 |
| torch.from_numpy(ndarray) | 将numpy.ndarray转换为Tensors |
| torch.normal(means,std,out=None) | 返回一个离散分布中抽取随机数 |
索引、切片、连接、换位
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.cat(inputs,dimension=0) | 在给定维度上对inputs进行拼接 |
| torch.chunk(tensor,chunks,dim=0) | 在给定维度上对tensor进行分块 |
| torch.split(tensor,split_size,dim=0) | 在给定维度上对tensor进行分块 |
| torch.squeeze(input,dim=None,out=None) | 去除输入张量形状中的1并返回 |
| torch.stack(sequence,dim=0) | 沿着新维度对输入张量序列进行拼接 |
| torch.t(input,out=None) | 对input矩阵进行转置 |
| torch.transpose(input,dim0,dim1,out=None) | 交换input的dim0与dim1 |
| torch.unbind(tensor,dim=0) | 移除指定维度,返回包含沿指定维度切片后的各个切片 |
| torch.unsqueeze(input,dim,out=None) | 返回一个新张量,对输入的位置插入维度1 |
序列化、反序列化
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.save( ) | 保存一个对象到一个硬盘文件上 |
| torch.load( ) | 从磁盘文件中读取一个通过torch.save()保存的对象b |
并行化
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.get_num_threads( ) | 获取用于并行化CPU操作的OpenMP线程数 |
| torch.set_num_threads( ) | 设定用于并行化CPU操作的OpenMP线程数s |
数学操作
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.div(input,value,out=None) | 将input逐元素除以标量value |
| torch.exp(tensor,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的指数 |
| torch.abs(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的绝对值 |
| torch.sin(input,out=None) | 计算每个元素的正弦值 |
| torch.cos(input,out=None) | 计算每个元素的余弦值 |
| torch.atan(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的反正切 |
| torch.asin(input,out=None) | 计算每个元素的反正弦 |
| torch.acos(input,out=None) | 计算每个元素的反余弦 |
| torch.cosh(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的双曲余弦 |
| torch.add(input,value,out=None) | 对input逐元素加上标量value |
| torch.addcdiv(tensor,value,tensor1,tensor2,out=None) | 用tensor2对tensor1逐元素相除,乘以value并加到tensor |
| torch.addcmul(tensor,value,tensor1,tensor2,out=None) | 用tensor2对tensor1逐元素相乘,乘以value,然后加到tensor |
| torch.floor(input,out=None) | 对input每个元素向下取整 |
| torch.ceil(input,out=None) | 对input每个元素向上取整 |
| torch.clamp(input,min,max,out=None) | 将input每个元素夹紧至【min,max】内 |
| torch.fmod(input,divisor,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的除法余数 |
| torch.frac(tensor,out=None) | 返回每个元素的分数部分 |
| torch.log(input,out=None) | 计算log的自然对数 |
| torch.mul(input,value,out=None) | 将input逐元素乘以标量value |
| http://torch.net(input,out=None) | 将input逐元素取负 |
| torch.pow(input,exponent,out=None) | 将input逐元素求exponent次幂 |
| torch.reciprocal(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的倒数 |
| torch.remainder(input,divisor,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的除法余数 |
| torch.round(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素四舍五入后的值 |
| torch.rsqrt(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的平方根倒数 |
| torch.sigmoid(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的sigmoid值 |
| torch.sign(input,out=None) | 返回input每个元素的符号 |
| torch.sqrt(input,out=None) | 计算input每个元素的平方根 |
| torch.trunc(input,out=None) | 将input每个元素的小数部分截断 |
| torch.cumprod(input,dim,out=None) | 沿着dim维度计算input累积积 |
| torch.cumsum(input,dim,out=None) | 沿dim维度计算input累计和 |
| torch.dist(input,other,p=2,out=None) | 返回(input-other)的p范数 |
| torch.mean(input) | 计算input所有元素的均值 |
| torch.mean(input,dim,out=None) | 计算input指定维度所有元素的均值 |
| torch.median(input,dim=-1,values=None,indices=None) | 返回input给定维度所有元素的中位数,同时返回一个包含中位数的索引的LongTensor |
| torch.mode(input,dim,values=None,indices=None) | 返回给定维度所有元素的众数,同时返回一个包含众数索引的LongTensor |
| torch.norm(input,p,dim,out=None) | 返回input的p范数 |
| torch.prod(input,dim) | 返回input所有元素的积 |
| torch.std(input,dim) | 返回input所有元素的标准差 |
| torch.sum(input,dim) | 返回input所有元素的和 |
| torch.var(input,dim) | 返回input在给定维度上每个元素的方差b |
比较操作
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.eq(input,other,out=None) | 比较input每个元素是否与other相等 |
| torch.equal(tensor1,tensor2) | 比较tensor1与tensor2是否完全相等 |
| torch.ge(input,other,out=None) | 逐元素比较input和other |
| torch.gt(input,other,out=None) | 逐元素比较input和other |
| torch.kthvalue(input,k,dim=None,out=None) | 取输入张量input指定维度上第K个最小值 |
| torch.le(input,other,out=None) | 逐元素比较input和other |
| torch.lt(input,other,out=None) | 逐元素比较input和other |
| torch.max(input,dim) | 返回input给定维度上的最大值 |
| torch.min(input,dim) | 返回input给定维度上的最小值 |
| torch.ne(input,other) | 逐元素比较input和other |
| torch.sort(input,dim=None,descending=False,out=None) | 对输入张量input沿着指定维度按升序排序 |
| torch.topk(input,k,dim=None,largest=True,out=None) | 沿指定维度返回input中K个最大值q |
其他操作
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.cross(input,other,dim,out=None) | 沿着指定维度计算input与other的向量积 |
| torch.dot(tensor1,tensor2) | 计算两个张量的内积 |
| torch.eig(a,eigenvectors=False,out=None) | 计算方阵a的特征值和特征向量 |
| torch.inverse(input,out=None) | 对方阵input取逆 |
| torch.mm(mat1,mat2,out=None) | 计算mat1与mat2的乘积 |
| torch.mv(mat,vec,out=None) | 计算矩阵与向量vec的乘积 |
| torch.abs_(input) | torch.abs(input)的in-place运算形式 |
3.2 torch.nn

参数设置
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| torch.nn.Parameter(data,requires_grad) | 将不可训练的data转换为可训练的类型parameter,并将这个parameter绑定到module内 |
torch.nn.Module基类
| 函数 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
| add_module(name,module) | 将一个child module添加到当前module,可通过name属性获取module |
| cuda(device_id=None) | 将所有模型参数复制到GPU |
| cpu(device_id=None) | 将所有模型参数复制到CPU |
| double() | 将parameters和buffers的数据类型转换为double |
| float() | 将parameters和buffers的数据类型转换为float |
| half() | 将parameters和buffers的数据类型转换为half |
| eval() | 将模型设置成evaluation模式 |
| train(mode=True) | 将module设置为training mode |
| forward(*input) | 定义了每次执行的计算步骤,在所有子类中都需要重写这个函数 |
| modules() | 返回一个包含当前模型所有模块的迭代器 |
| named_modules() | 返回包含网络中所有模块的迭代器 |
| children() | 返回当前模型子模块的迭代器 |
| named_children() | 返回包含模型当前模块的迭代器 |
| load_state_dict(state_dict) | 加载模型参数,将state_dict中的parameters和buffers复制到module和他的后代中 |
| parametes(memo=None) | 返回一个包含模型所有参数的迭代器 |
| register_backward_hook(hook) | 在module上注册一个backward hook,hook(module,grad_input,grad_output) |
| register_forward_hook(hook) | 在module上注册一个forward hook,hook(module,input,output) |
| register_buffer(name,tensor) | 给module添加一个永久buffer |
| register_parameter(name,param) | 向module添加parameter |
| state_dict() | 返回一个保存着module所有状态的字典 |
| zero_grad() | 将module中所有模型参数的梯度设置为0 |
| torch.nn.Sequential(*args) | 一个时序容器,modules会以它们传入的顺序被添加到容器中,也可以传入一个orderedDict |
| torch.nn.ModuleList(modules=None) | 将submodules保存在一个list中 |
| append(module) | 等价与list中的append |
| extend(modules) | 等价于list中的extend |
| torch.nn.ParameterList(parameters=None) | 将submodules保存在一个list中 |
卷积层
torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride,padding,dilation,groups,bias)
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride,padding,dilation,groups,bias)
torch.nn.Conv3d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride,padding,dilation,groups,bias)
torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride,padding,groups,bias)
torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride,padding,groups,bias)
torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride,padding,groups,bias)
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| in_channels | 输入信号的信道 |
| out_channels | 卷积产生的通道 |
| kernel_size(int or tuple) | 卷积核尺寸 |
| stride(int,tuple,optional) | 卷积步长 |
| padding(int or tuple,optional) | 输入的每一条边补充0的层数 |
| dilation(int or tuple,optional) | 卷积核元素之间的间距 |
| groups(int,optional) | 从输入通道到输出通道的阻塞连接数 |
| bias(bool,optional) | 是否添加偏置 |
池化层
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size,stride,padding,dilation,return_indices,ceil_mode)
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size,stride,padding,dilation,return_indices,ceil_mode)
torch.nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size,stride,padding,dilation,return_indices,ceil_mode)
torch.nn.AvgPool1d(kernel_size,stride,padding,ceil_mode,count_include_pad)
torch.nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size,stride,padding,ceil_mode,count_include_pad)
torch.nn.AvgPool3d(kernel_size,stride,padding,ceil_mode,count_include_pad)
torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool1d(output_size,return_indices=False)
torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(output_size,return_indices=False)
torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool3d(output_size,return_indices=False)
torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(output_size)
torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size)
torch.nn.MaxUnpool1d(kernel_size,stride=None,padding=0)
torch.nn.MaxUnpool2d(kernel_size,stride=None,padding=0)
torch.nn.MaxUnpool3d(kernel_size,stride=None,padding=0)
torch.nn.FractionalMaxPool2d(kernel_size,output_size,output_ratio,return_indices,_random_samples)
torch.nn.LPPool2d(norm_Type,kernel_size,stride,ceil_mode)
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| kernel_size(int or tuple) | max pooling的窗口大小 |
| stride(int,tuple,optional) | max pooling的窗口移动步长 |
| padding(int or tuple,optional) | 输入的每一条边补充0的层数 |
| dilation(int or tuple,optional) | 控制窗口中元素的字符 |
| return_indices | 为True时,会返回输出最大值的序号 |
| ceil_mode | 为True时,计算输出信号的大小时使用向上取整 |
| count_include_pad | 为True时,计算平均池化时,将包括padding填充的0 |
| output_size | 输出信号的尺寸 |
| return_indices | 为True时,会返回输出的索引,对nn.MaxUnpool有用 |
| output_ratio | 将输入图像大小的百分比指定为输出图像的大小 |
非线性激活函数
| torch.nn.ReLU() |
|---|
| torch.nn.ELU(alpha=1.0,inplace=Flase) |
| torch.nn.PReLU(num_parameters=1,init=0.25) |
| torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01,inplace=False) |
| torch.nn.Threshold(threshold,value,inplace=False) |
| torch.nn.Hardtanh(min_value=-1,max_value=1,inplace=False) |
| torch.nn.Sigmoid() |
| torch.nn.Tanh() |
| torch.nn.LogSigmoid() |
| torch.nn.Softplus(beta=1,threshold=20) |
| torch.nn.Softshrink(lambda=0.5) |
| torch.nn.Softsign() |
| torch.nn.Softmin() |
| torch.nn.Softmax() |
| torch.nn.LogSoftmax() |
正则化
| torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features,eps=1e-05,momentum=0.1,affine=True) |
|---|
| torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features,eps=1e-05,momentum=0.1,affine=True) |
| torch.nn.BatchNorm3d(num_features,eps=1e-05,momentum=0.1,affine=True) |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| num_features | 来自期望输入的特征数,该期望输入的大小为batch_size*num_features |
| eps | 为保证数值稳定性,给分布加上的值 |
| momentum | 动态均值和动态方差所使用的动量 |
| affine | 为True时,给该层添加学习的仿射变换参数x |
循环层 RNN 系列
循环层
| torch.nn.RNN(input_size,hidden_size,num_layers=1,nonlinearity=tanh,bias=True,batch_first=False,dropout=0,bidirectional=False) |
|---|
| torch.nn.LSTM(input_size,hidden_size,num_layers=1,nonlinearity=tanh,bias=True,batch_first=False,dropout=0,bidirectional=False) |
| torch.nn.GRU(input_size,hidden_size,num_layers=1,nonlinearity=tanh,bias=True,batch_size=False,dropout=0,bidirectional=False) |
| torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size,hidden_size,bias=True,nonlinearity=’tanh’) |
| torch.nn.LSTMCell(input_size,hidden_size,bias=True,nonlinearity=’tanh’) |
| torch.GRUCell(input_size,hidden_size,bias=True,nonlinearity=’tanh’) |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| input_size | 输入特征的维度 |
| hidden_size | 隐藏层神经元个数 |
| num_layers | 网络的层数 |
| nonlinearity | 激活函数 |
| bias | 是否使用偏置 |
| batch_first | 输入数据的形式 |
| dropout | 是否使用dropout |
| bidirectional | 是否使用双向RNN |
线性层 Linear
正常的线性计算:
y = X · W + b
pytorch内的线性计算:【以数据转置的形式存在】
y = X · W.T + b
原因:
- 图像处理时候让卷积操作和全连接层(线性层)工作方式保持一致。
线性层
torch.nn.Linear(in_features,out_features,bias=True)
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| in_features | 输入样本的大小 |
| out_features | 输出样本的大小 |
| bias | 为False时,不学习偏置c |
参数详解
- 1、in_features:输入的最后一维的通道个数
- 比如如果输入的数据是N*10的矩阵,表示有N条数据,10个特征,那么in_features应设置为10。
- 2、out_features:输出的最后一维的通道个数
- 比如如果输出的数据是10*3的矩阵,表示有10条数据,3个特征,那么out_features应设置为3。
- 3、bias:线性回归方程的偏置量
- 默认为True,也就是包含偏置项,这也是多数情况的选择。
import torch
# 数据:3*2
data = torch.Tensor([[1.0, 2.0],
[7.0, 8.0],
[4.0, 5.0]])
# 定义输入为2列,输出为3列
my_nn = torch.nn.Linear(2,3)
my_nn1 = torch.nn.Linear(3,10)
# 输出 :3*3
out = my_nn(data)
print(out)
# 查看权重: 权重矩阵3*2,pytorch将数据以转置的形式存储,并且不会影响正常网络运转。
print(my_nn.weight)
# 既显示权重,又显示偏置
print(list(my_nn.parameters()))
out1 = my_nn2(out) # 多个 MLP 叠加
# 提取权重参数
tmp_v = my_nn1.weight.data.T
裁剪层 Dropout
裁剪层
| torch.nn.Dropout(p,inplace=False) |
|---|
| torch.nn.Dropout2d(p,inplace=False) |
| torch.nn.Dropout3d(p,inplace=False) |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| p | 将元素置0的概率 |
| inplace | 为True时,会原地执行操作i |
稀疏层
稀疏层
| torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings,embedding_dim,padding_idx=None,max_norm=None,norm_type=2,scale_grad_by_freq=False,sparse=False) | | — |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| num_embeddings(int) | 嵌入字典的大小 |
| embedding_dim(int) | 每个嵌入向量的大小 |
| padding_idx(int,optional) | 如果提供的话,输出遇到此下标时用零填充 |
| max_norm(float,optional) | 如果提供的话,会重新归一化词嵌入,使它们的范数小于提供的值 |
| norm_type(float,optional) | 对于max_norm选项计算P范数时的p |
| scale_grad_by_freq(bollean,optional) | 如果提供的话,会根据字典中单词频率缩放梯度j |
距离函数
| torch.nn.PairwiseDistance(p=2,eps=1e-06) | | — |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| p | 范数次数s |
损失函数
损失函数
| torch.nn.L1Loss(size_average=True) |
|---|
| torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.NLLLoss(weight=None,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.NLLLoss2d(weight=None,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.KLDivLoss(weight=None,size_average=Ture) |
| torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss(size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss(weight=None,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0,size_average=True) |
| torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss(p=1,margin=1,weight=None,size_average=True)c |
MSELoss
作用:
- 计算两个输入对应元素差值平方和的均值
默认值(最常用):
- reduction=’mean’,可选:’sum’、’none’
函数效果类似于 torch.mean((y-y')**2)
torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
示例
import torch
# 真实值
y = [[[0, 0],
[0, 0], ],
[[0, 0],
[0, 0], ]]
y = torch.tensor(y, dtype=torch.float)
# 预测值
y_pr = [[[1, 2],
[3, 4], ],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8], ]]
y_pr = torch.tensor(y_pr, dtype=torch.float)
# 1、利用torch自带的损失
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # 所有样本损失的均值
# loss = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum') # 所有样本损失的和
# loss = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='none') # 返回每个样本的损失,tensor格式的矩阵
losss = loss(y, y_pr)
print(losss)
# 2、自己暴力计算
mean_result = (1 * 1 + 2 * 2 + 3 * 3 + 4 * 4 + 5 * 5 + 6 * 6 + 7 * 7 + 8 * 8)/ 8
print(mean_result)
# 3、利用torch的mean函数
print(torch.mean((y - y_pr) ** 2))
视觉层
视觉层
| torch.nn.PixelShuffle(upscale_factor) |
|---|
| torch.nn.UpsamplingNearest2d(size=None,scale_factor=None) |
| torch.nn.UpsamplingBilnear2d(size=None,scale_factor=None)s |
多GPU层
| torch.nn.DataParallel(module,device_ids=None,output_device=None,dim=0)gon | | — |
工具函数
| torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm(parameters,max_norm,norm_type=2) |
|---|
| torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence(_cls,data,batch_sizes) |
| torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(input,lengths,batch_first=False) |
| torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_packed_sequence(sequence,batch_first=False) |
3.3 torch.nn.functional
包含与torch.nn相对的所有实现;只不过torch.nn.functional是以函数形式封装的这些实现。
| torch.nn.X | torch.nn.functional |
|---|---|
| 类 | 函数 |
| 结构中包含所需要初始化的参数 | 需要在函数外定义并初始化相应参数,并作为参数传入 |
| 一般情况下放在init中实例化,并在forward中完成操作 | 一般在init中初始化相应参数,在forward中传入 |
3.4 torch.nn.autograd
| torch.autograd.backward(variables,grad_variables,retain_variables=False) | | — |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| variables | 将计算导数的变量 |
| grad_variables | 渐变写入相应变量的每个元素 |
| retain_gradph | 若为False,则用于计算grad的图形将被释放 |
| create_grahp | 若为True,则构造导数的图形 |
| torch.autograd.grad(outputs,inputs,grad_outputs=Noneretain_graph=None,create_graph=None,only_inputs=True) | | — |
| 参数 | 参数意义 |
|---|---|
| outputs | 差分函数的输出 |
| inputs | 输入将返回梯度的积分 |
| grad_outputs | 渐变wrd每个输出 |
| retain_graph | 若为False,则用于计算grad的图形被释放 |
| create_graph | 若为True,则构造导数的图形 |
| only_inputs | 若为True,则渐变wrt离开时图形的一部分,但不显示inputs不会被计算和累积 |
| torch.autograd.Function | | — |
记录操作历史并定义用于区分操作的公式
3.5 torch.optim
优化包括: 优化损失函数,优化神经网络中的参数计算方式。
| torch.optim.Optimizer(params,default) | | — |
所有优化器的基类
| 函数 | 函数意义 |
|---|---|
| load_state_dict(state_dict) | 加载optimizer状态 |
| state_dict() | 以dict类型返回optimizer状态 |
| step(closure) | 进行单步优化 |
| zero_grad() | 清空所有被优化过的Variable的梯度 |
| 优化器 | 优化器意义 |
|---|---|
| torch.optim.Adadelta(params,lr=1.0,rho=0.9,eps=1e-06,weight_decay=0) | 实现Adadelta算法 |
| torch.optim.Adagrad(params,lr=0.01,lr_decay=0,weight_decay=0) | 实现Adagrad算法 |
| torch.optim.Adam(params,lr=0.001,betas=(0.9,0.999),eps=1e-08,weight_decay=0) | 实现Adam算法 |
| torch.optim.Adamax(params,lr=0.002,betas=(0.9,0.999),eps=1e-08,weight_decay=0) | 实现Adamax算法 |
| torch.optim.ASGD(params,lr=0.01,lambd=0.0001,alpha=0.75,t0=1000000.0,weight_decay=0) | 实现平均随机梯度下降算法 |
| torch.optim.LBFGS(params,lr=1,max_iter=20,max_eval=None,tolerance_grad=1e-05,tolerance_change=1e-09,history_size=100,line_search_fn=None) | 实现L-BFGS算法 |
| torch.optim.RMSprop(params,lr=0.01,alpha=0.99,eps=1e-8,weight_decay=0,momentum=0,centered=False) | 实现RMSprop算法 |
| torch.optim.Rprop(params,lr=0.01,etas=(0.5,1.2),step_sizes=(1e-06,50)) | 实现弹性反向传播算法 |
| torch.optim.SGD(params,lr,momentum=0,dampening=0,weight_decay=0,nesterov=False) | 实现随机梯度下降算法 |
理论
一阶矩和二阶矩
- 一阶矩: 期望,平均值
- 一阶中心矩: 每个数字与期望(均值)的期望(均值)
- 二阶矩
- 二阶原点矩: 平方差求和后的均值
- 二阶中心矩: 每个数据与数据均值的差的平方和的均值,简称方差
Adam
Adam(Adaptive momentum)是一种自适应动量的随机优化方法(A method for stochastic optimization)
参数解释
已经给定值的参数
- α:学习率,0.001
- β1 :一阶矩衰减系数,0.9
- β2 :二阶矩衰减系数,0.999
- ε:防止分母为0,10**-8
其他参数
- t:循环次数
- θ:要求解(更新)的参数
- f(θ):损失函数
- gt:损失函数对θ求导所得的梯度
- mt:gt的一阶原点矩
- vt:gt的二阶原点矩
- 𝑚t^:mt的偏置矫正
- vt^:vt的偏置矫正
Adam函数参数如下:
torch.optim.Adam(params, lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999),
eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0, amsgrad=False)
参数详解
- 1、
params返回模型中所有可训练参数的迭代器,包括权重和偏置,可通过循环进行调用。后续在预训练模型中经常使用与调整。 - 2、
lr学习率,我们自行设定。默认值0.001。一般按默认值设定即可。 - 3、
betas用于计算梯度的一阶矩估计和二阶矩估计的衰减因子。默认为(0.9, 0.999),也就是说β1为0.9,β2为0.999。本质是对于新梯度的融入程度的选择,一般按默认。 - 4、
eps为了数值稳定性而添加到分母中的小常数。防止除零错误。默认1e8。按默认,无需调整。 - 5、
weight_decayweight_decay指权重衰减,它是一种正则化项,用于减少模型的过拟合风险。权重衰减会惩罚模型中较大的权重值,以鼓励模型学习简单的权重。复杂模型可以设置该参数,确保模型不出现过拟合风险。 - 6、
amsgrad是否使用 AMSGrad 变种。当设置为 True 时,AMSGrad 变种保留了梯度的历史信息,这有助于一些情况下防止学习率过早下降。默认为False。一般按默认。
3.6 torch.nn.init
| torch.nn.init.calculate_gain(nonlinearity,param=None) |
|---|
| torch.nn.init.uniform(tensor,a=0,b=1) |
| torch.nn.init.normal(tensor,mean=0,std=1) |
| torch.nn.init.constant(tensor,val) |
| torch.nn.init.eye(tensor) |
| torch.nn.init.dirac(tensor) |
| torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform(tensor,gain=1) |
| torch.nn.init.xavier_normal(tensor,gain=1) |
| torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform(tensor,a=0,mode=’fan_in’) |
| torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal(tensor,a=0,mode=’fan_in’) |
| torch.nn.init.orthogonal(tensor,gain=1) |
3.7 torch.multiprocessing
用于在相同数据的不同进程中共享视图
3.8 torch.cuda
实现与CPU张量相同的功能,但使用GPU进行计算
| 函数 | 函数意义 |
|---|---|
| torch.cuda.current_blas_handle() | 返回cublasHandle_t指针 |
| torch.cuda.current_device() | 返回当前设备 |
| torch.cuda.device(idx) | 上下文管理器,可以更改所选设备 |
| torch.cuda.device_count() | 返回可获得的GPU数量 |
| torch.cuda.device_of(obj) | 将当前设备更改为给定对象的上下文管理器 |
| torch.cuda.is_available() | 指示CUDA当前是否可用 |
| torch.cuda.set_device(device) | 设置当前设备 |
| torch.cuda.stream(stream) | 选择给定流的上下文管理器 |
| torch.cuda.synchronize() | 等待当前设备上所有流中的所有核心完成 |
| torch.cuda.comm.broadcast(tensor,devices) | 向一些GPU广播张量 |
| torch.cuda.comm.reduce_add(inputs,destination=None) | 将来自多个GPU的张量相加 |
| torch.cuda.comm.scatter(tensor,devices,chunk_sizes=None,dim=0,streams=None) | 打散横跨多个GPU的张量 |
| torch.cuda.comm.gather(tensors,dim=0,destination=None) | 从多个GPU收集张量 |
| torch.cuda.Stream | CUDA流的包装 |
3.9 torch.utils
torch.utils.data.Dataset
表示Dataset的抽象类,所有子类应该override_len_和_getitem_,前者提供了数据集的大小,后者支持整数索引。
| 函数 | 函数意义 |
|---|---|
| torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(data_tensor,target_tensor) | 包装数据和目标张量的数据集 |
| torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset,batch_size,shuffle,sampler,num_workers,collate_fn,pin_memory,drop_last) | 数据加载器,组合数据集和采集器,并在数据集上提供单进程或多进程迭代器 |
torch.utils.data.sampler.Sampler(data_source)
所有采样器的基础类,每个采样器子类必须提供一个_iter_方法,提供一种迭代数据集元素的索引的方法,以及返回迭代器长度的_len_方法
| 函数 | 函数意义 |
|---|---|
| torch.utils.data.sampler.SequentialSampler(data_source) | 样本元素顺序排列,始终以相同的顺序 |
| torch.utils.data.sampler.RandomSampler(data_source) | 样本元素随机,没有替换 |
| torch.utils.data.sampler.SubsetRandomSampler(indices) | 样本元素从指定的索引列表中随机抽取,没有替换 |
| torch.utils.data.sampler.WeightedRandomSampler(weights,num_samples,replace=True) | 样本元素来自于【0,len(weights)-1】,给定概率 |
| torch.utils.model_zoo.load_url(url,model_dir=None) | 在给定的URL上加载Torch序列化对象 |
3.10 torch.torchvision
内含数据集
| torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root,train=True,transform=None,target_transform=None,download=False) |
|---|
| torchvision.datasets.CocoCaptions(root=’dir where images are’,annFile=’json annotation file’,[transform,target_transform]) |
| torchvision.datasets.CocoDetection(root=’dir where images are’,annFile=’json annotation file’,[transform,target_transform]) |
| torchvision.datasets.LUSN(db_path,classes=’train’,[transform,target_transform]) |
| torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(root=’root_folder path’,[transform,target_transform]) |
| torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root,train=True,transform=None,target_transform=None,download=False) |
| torchvision.datasets.CIFAR100(root,train=True,transform=None,target_transform=None,download=False) |
| torchvision.datasets.STL10(root,split=’train’,transform=None,target_transform=None,download=False)n |
内含模型
| torchvision.models.alexnet(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
|---|
| torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.resnet34(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.resnet50(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.resnet101(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.resnet152(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg11(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg11_bn(**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg13(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg13_bn(**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg16_bn(**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg19(pretrained=False,**kwargs) |
| torchvision.models.vgg19_bn(**kwargs)sh |
数据预处理
| torchvision.transforms.Compose(transforms) |
|---|
| torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(size) |
| torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop(size,padding=0) |
| torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip |
| torchvision.transforms.RandomSizedCrop(size,interpolation=2) |
| torchvision.transforms.Pad(padding,fill=0) |
| torchvision.transform.Normalize(mean,std) |
| torchvision.transforms.ToTensor |
| torchvision.transforms.ToPILImage |
| torchvision.transforms.Lambda(lambda) |
| torchvision.utils.make_grid(tensor,nrow=8,padding=2,normalize=False,range=None,scale_each=False) |
| torchvisin.utils.save_image(tensor,filename,nrow=8,padding=2,normalize=False,range=None,scale_each)x |
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏 
