- DeepSpeed 学习笔记
- 结束
DeepSpeed 学习笔记
deepspeed 知识点
为什么
混合精度训练的迭代流程
PyTorch 里的 DataParallel 无法满足
模型并行和流水线并行实现相对复杂,需要模型拆分、卡间通讯等。以及优化显存占用门槛高。
这也是 DeepSpeed 设计初衷。
DeepSpeed 框架演进
【2024-4-6】总结:
Megatron – NVIDIA
Megatron is a large, powerful transformer developed by the Applied Deep Learning Research team at NVIDIA. This repository is for ongoing research on training large transformer language models at scale. We developed efficient, model-parallel (tensor, sequence, and pipeline), and multi-node pre-training of transformer based models such as GPT, BERT, and T5 using mixed precision.
【2023-7-27】大模型-LLM分布式训练框架总结
Megatron-LM 介绍
【2020-3-13】Megatron 是超大规模 Transformer 模型 分布式训练解决方案。
字节、阿里和快手等公司都将其作为大模型训练框架。
- 论文: Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism
- 中文解读: Megatron论文和代码详细分析
- intra-layer and inter-layer: 层间并行和层内并行
- orthogonal and complimentary 正交和互补
- scaling efficiency 计算公式 76%
| 概念 | 中文 | 图解 |
|---|---|---|
| intra-layer and inter-layer | 层间并行和层内并行 | 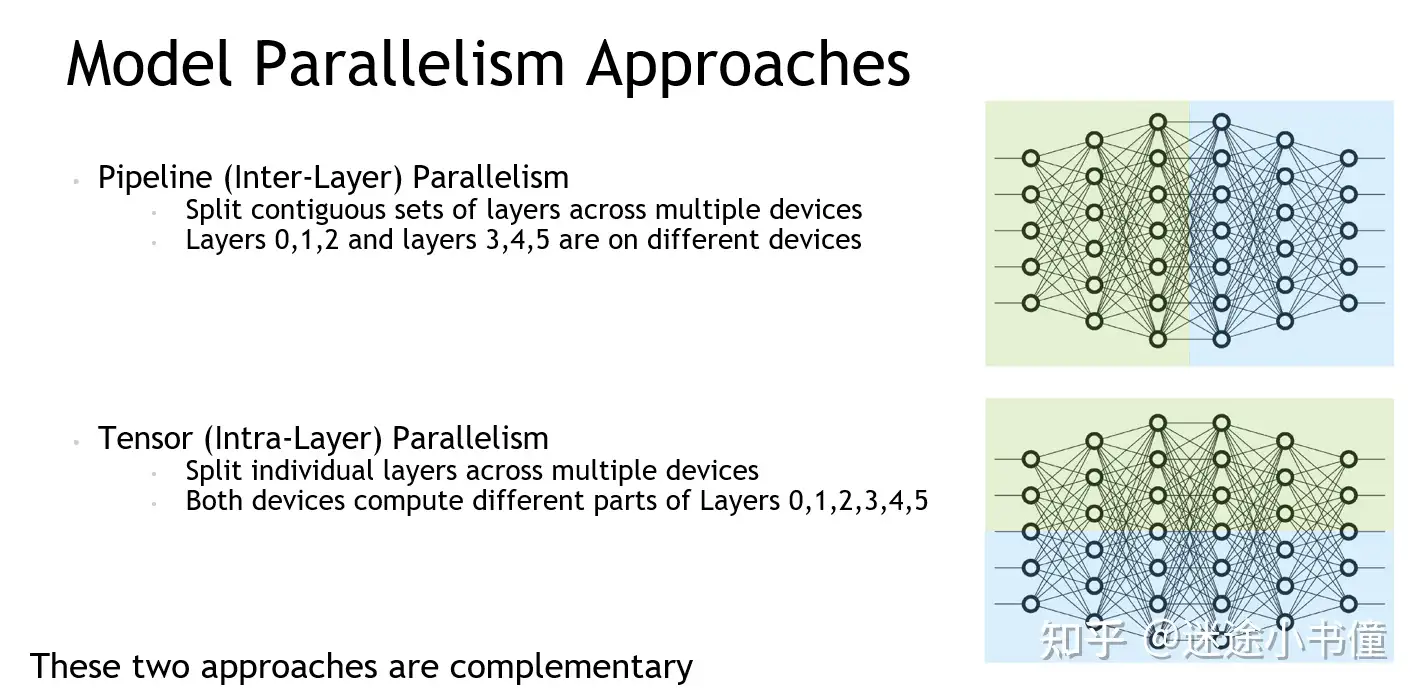 |
| orthogonal and complimentary | 正交和互补 | 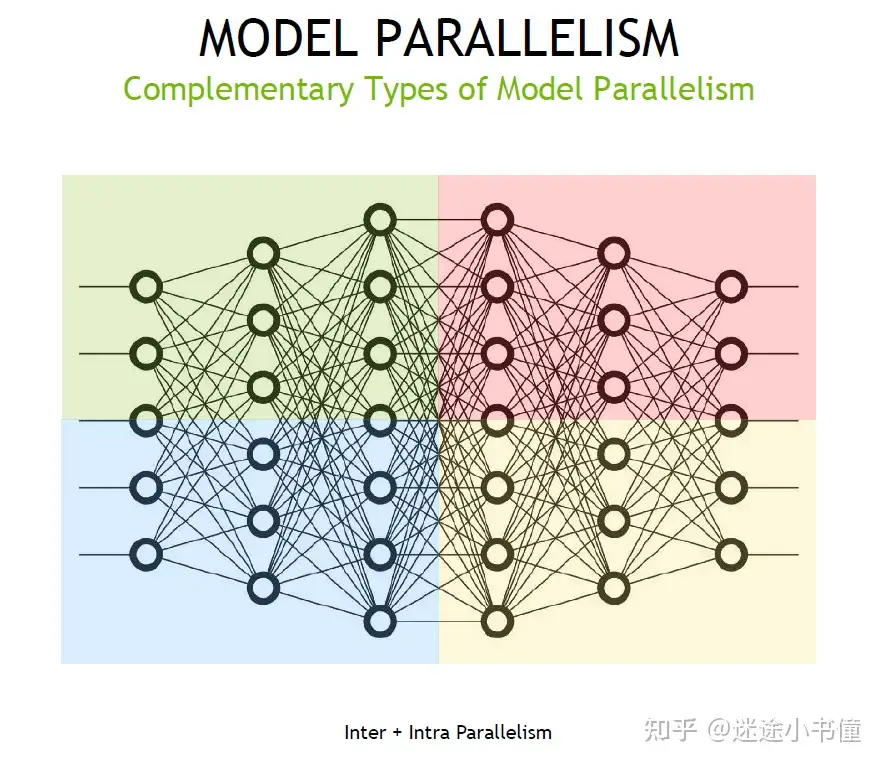 |
Megatron 核心能力:
- 多种并行策略组合: Data Parallel、 Tensor Parallel、Pipeline Parallel、Sequence Parallel
- Distributed-optimiezer: 相当于 deepspeed zero1 策略
- 高性能算子:Flash Attention
- Activation checkpoint
- 混合精度
- Gradient accumulation
- MoE
Megatron-LM
- 1). Megatron-LM-1
- 2). Megatron-LM-2
- 3). Megatron-LM-3
Megatron-LM-1
利用 张量并行和数据并行
Megatron-LM-2
Megatron 2 在 Megatron 1 的基础上新增 pipeline 并行,提出了 virtual pipeline:1F1B-interleaving,成为和 DeepSpeed 类似的 3D 并行训练框架。
另外 Megatron-2 论文提及了一些通信优化的小 trick,本质是增加本地的 io 操作和通信,从而降低低带宽网络的通信量。
内存占用角度:
G-pipe到PipeDream进化完成,通过及时安排反向过程,将前向激活值释放掉,避免积累太多激活值占用内存,提高了模型并行的能力。
空泡比率角度:
- 空泡比率的提升主要从
1F1B到1F1B-interleaving进化得来。
pipeline 并行的基本规律:
- pipeline 流水级数越多, overhead(开销) 就越大。
如何计算空泡率?参考
- 阴影部分所表示的时间段里,总有GPU在空转。Gpipe中,将阴影部分定义为bubble
- 假设有 K 块GPU,而单块GPU上做一次forward和backward的时间为:t_fb = t_f + t_b
- 空泡率:
(K-1)K*t_fb/K*K*t_fb=(K-1)/K
bubble部分的时间复杂度为: O((K-1)/K)
- 当K越大,即GPU越多,空置比例接近1,GPU资源都被浪费掉了
模型并行训练:Megatron-LM pipeline并行源码解读
pipeline并行状态 parallel_state
get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size:pipeline并行的卡数get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank:当前卡在pipeline并行中的序号is_pipeline_last_stage(ignore_virtual=True)+is_pipeline_first_stage(ignore_virtual=True): 忽略virtual stage时,判断当前stage是否为流水线并行的最后一个、第一个stage。
如下图,红色框均为 first stage,黄色框均为 last stage。
p2p_communication,主要功能两个事情:发送 send 和 接受 recv。
forward:- 从前面的stage 获取中间结果: 前面stage的output tensor,做为当前stage的 input tensor,这个操作对于当前stage称为recv,具体为recv_forward;
- 之后,需要当前stage的输出发送到后面的stage,这个操作对于当前stage是send,具体为send_forward。
backward:- backward之前,需要从前面的stage获取recv中间结果的梯度,recv_backward;
- backward之后,需要将输入的梯度send到后面的stage去,send_backward。
forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving 调度过程分成三个部分:warmup、1F1B、cooldown。
- 第一条红线左边是
warmup,第二条红线右边是cooldown,中间是1F1B。 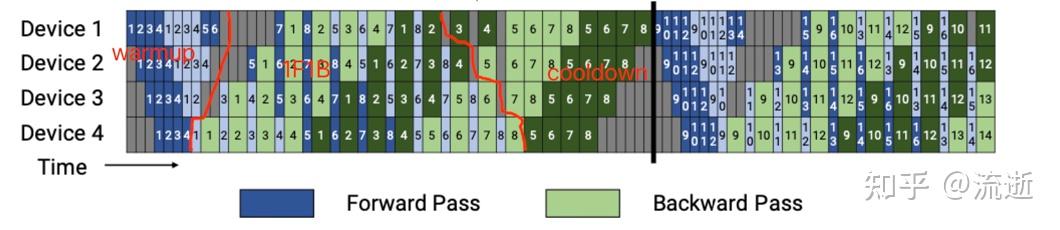
forward_only 情况比 forward+backward 的情况要简单。
warmup
- warmup只做forward。
- warmup内,又分为三种情况,第一个、最后一个、中间。
- 第一个:forward跑之前去做一次recv_forward;跑完做一次send_forward_recv_backward,send当前stage的output tensor,recv下一个stage的input tensor。
- 中间:跑完forward之后做一次send_forward_recv_forward,send当前stage的output tensor,recv下一次的input tensor。
- 最后一个:跑完forward之后做一次send_forward_recv_forward_backward,send当前的output tensor,recv下一次的input tensor,recv 1F1B中第一个backward使用的输入。
1F1B
- 1F1B,一次forward一次backward,轮流交替进行。
- 先 forward + backward
- 然后 send_forward_backward_recv_forward_backward,recv的是下一次1F1B用到的输入输出,最后一次1F1B这里需要特判一下。
cooldown
- cooldown只做backward。
- 先backward,然后send_backward_recv_backward,特判最后一次不需要recv。
调度策略
- default 调度 和 interleaved 调度
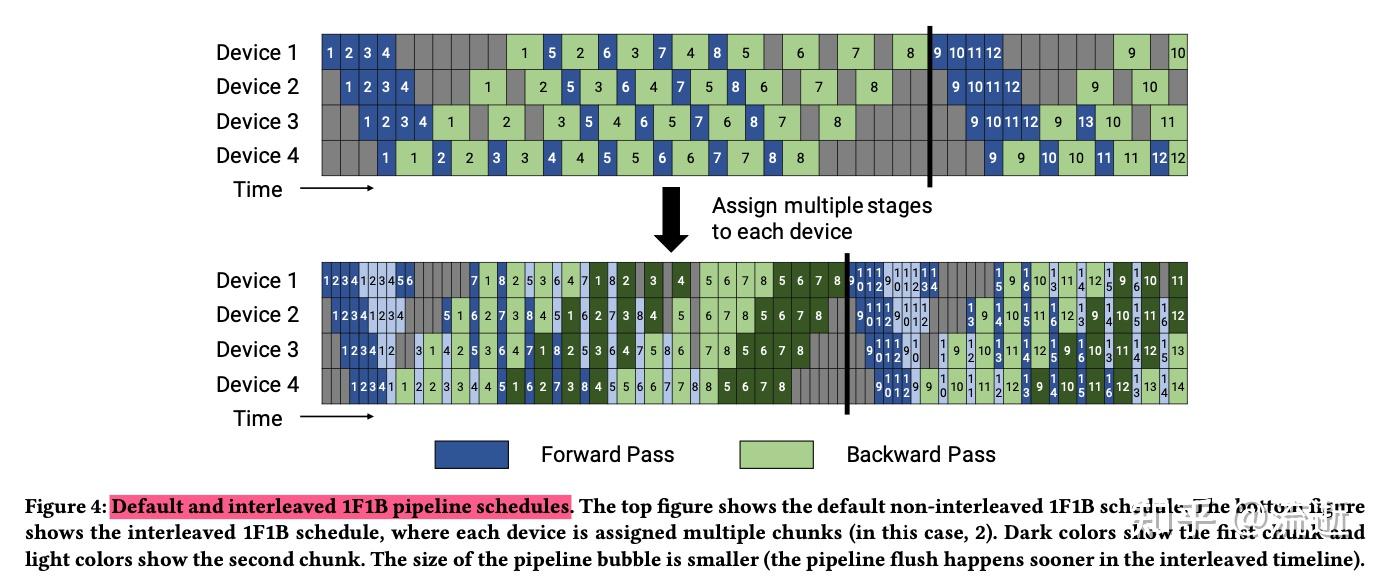
相同点:都分为 warmup、1F1B、cooldown 三个过程。
不同
- forward、backward 是否对齐
- default 时,不同device上的forward、backward 不对齐;
- 而interleaved 是对齐的。
- 一个forward 做完后是否立即通信
- default 立刻开始通信,传递中间结果,下一个device需要紧接着使用它。
- interleaved 不需要立刻开始通信传递中间结果,下一个device需要先做一次backward才会做用到传递的中间结果。
Megatron-LM-3
增加三个feature:
Sequence Parallelism: Tensor Parallelism 基础上,将Transformer的LayerNorm以及Dropout层的输入按Sequence Length维度进行了切分,使得各个设备上面只需要做一部分的Dropout和LayerNorm。Selective Activation Recomputation去掉激活值重新计算Checkpointing Skipping: GPU显存没占满时候不做checkpointing
Megatron1, 2中,Transformer核的TP通信是由正向两个Allreduce以及后向两个Allreduce组成的。Megatron 3由于对sequence维度进行了划分,Allreduce在这里已经不合适
Checkpointing Skipping
Megatron-DeepSpeed
Megatron-DeepSpeed 结合两种主要技术:
DeepSpeed是微软开发的深度学习优化库,分布式训练变得简单、高效和有效。Megatron-LM是由NVIDIA的应用深度学习研究团队开发的大型、强大的 Transformer 模型框架。
DeepSpeed 团队通过将 DeepSpeed 库中的 ZeRO 分片(ZeRO sharding)和管道并行(pipeline parallelism)与 Megatron-LM 中的张量并行(Tensor Parallelism)相结合,开发了一种基于 3D 并行的实现。
Megatron-DeepSpeed 实施 3D 并行, 让大型模型训练更加高效。
DataParallel(DP) - 初始化模型被复制多次,并且每次都被馈送 minibatch 的一部分。处理是并行完成的,所有设置在每个训练步骤结束时进行同步。TensorParallel(TP) - 每个张量都被分成多个块,因此不是让整个张量驻留在单个 GPU 上,而是张量每个分片都驻留在其指定的 GPU 上。在处理过程中,每个分片在不同 GPU 上分别并行处理,最终结果在步骤结束时同步。这也被称作横向并行。PipelineParallel(PP) - 模型在多个 GPU 上垂直(层级)拆分,因此只有模型的一个或多个层放置在单个 GPU 上。每个 GPU 并行处理管道的不同阶段,并处理一小部分批处理。零冗余优化器(ZeRO) - 也执行与 TP 有点类似的张量分片,除了整个张量会及时重建以进行前向或反向计算,因此不需要修改模型。它还支持各种卸载技术以补偿有限的 GPU 内存。
各个技术细节参考:大型语言模型(LLM)训练指南
DeepSpeed 介绍
GPT-3把LLM参数量推到 175B,训练所需参数大小更是到达了万亿规模
- Megatron 开始变得无能为力
- 而 DeepSpeed ZeRO 方法问世, 解决了这个问题
DeepSpeed 安装
如何安装
直接pip安装:
pip install deepspeed
官方推荐仓库本地编译安装,更加适配本地硬件环境:
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/
cd DeepSpeed
rm -rf build
TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="8.6" DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 pip install . \
--global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v \
--disable-pip-version-check 2>&1 | tee build.log
检查
ds_report
HuggingFace
Transformers中,Trainer 集成核心 DeepSpeed 功能
HuggingFace 提供 DeepSpeed 集成,所需参数都可以由Transformer的Trainer自动指定。
- DeepSpeed 在 HuggingFace Transformer 上更为便捷(DeepSpeed 可独立使用,并不依赖于Transformer)。
作为 Transformer 附属包安装
pip install transformers[deepspeed]
如何使用
使用 DeepSpeed 后,命令行:
deepspeed --master_port 29500 --num_gpus=2 run_s2s.py \
--deepspeed ds_config.json
--master_port # 端口号。最好显示指定,默认为29500,可能会被占用(i.e., 跑了多个DeepSpeed进程)。
--num_gpus # GPU数目,默认会使用当前所见的所有GPU。
--deepspeed # 提供的config文件,用来指定许多DeepSpeed的重要参数。
使用 DeepSpeed 核心要点: 写一个config文件(.json,或json格式的配置文件)
- 指定想要的参数,例如,权衡时间和显存 (前文所提到的,这是一个很重要的权衡)。
因此,最重要的是 --deepspeed,即提供的config文件,即ZeRO。
【2023-9-16】DeepSpeed:炼丹小白居家旅行必备
deepspeed \
--launcher_args "source ${PWD}/setup_env.sh" \
--hostfile hostfile \
deepspeed_script.py \
--deepspeed \
--deepspeed_config "$PWD/deepspeed_config.json"
DeepSpeed 原理
DeepSpeed 核心思想:
GPU显存不够,CPU内存来凑
deepspeed 底层依赖 torch.distribution 、 cuda 等等.
底层分布式通信引擎支持多种选择
- [‘
cuda’, ‘cpu’, ‘xpu’, ‘npu’, ‘mps’] - 大部分选择 cuda, 可通过环境变量
DS_ACCELERATOR指定
入口(init)只是一个代理,根据不同情况选择三种模式之一
流水线引擎(PipelineEngine)混合引擎(DeepSpeedHybridEngine),同时进行训练和推理,为 RLHF 训练定制。一般模式(DeepSpeedEngine),基本模式,分布式训练引擎。
DeepSpeedEngine 的实现在 deepspeed.runtime.engine 中, 本身是 torch.nn.Module 的子类,对输入模型的一个封装。
- DeepSpeedEngine 的 init 方法中进行了大量初始化操作, 其中最重要的就是对优化器(Optimizer)的初始化, ZeRO 的核心特性的实现都在优化器(Optimizer)中。
DeepSpeed 适用情形
DeepSpeed 仅适用于:
- 显存极度短缺的情况;
- i.e., 模型大到
batch_size == 1也跑不了
- i.e., 模型大到
- 用DeepSpped节省下来的显存,刚好够支持更大的batch_size。
否则,使用 DeepSpeed 只会增加时间开销,并没有其他益处。
- stage3 速度极其缓慢。6h -> 48h
- 原先需要6h的训练过程,用 DeepSpeed stage3之后,运行了2天2夜,也没有结束的迹象。
- stage2 由于分配了模型参数到多个设备上,console 看不到任何输出信息(但是GPU还是在呼呼响,utility也为100%),不知道程序的运行进度,不友好。
由于 DeepSpeed 通过占用CPU内存来减缓GPU的开销,当系统CPU不够时,DeepSpeed 进程就会自动被系统停止,造成没有任何报错,DeepSpeed无法启动的现象。
- 建议用 estimation 估计一下CPU内存占用,然后用
free -h查看一下机器的CPU内存空余量,来判断能否使用DeepSpeed。
DeepSpeed 功能
DeepSpeed 支持多种训练优化策略:
- 3D并行:
数据并行、模型并行、流水线并行以及三者的混合使用 - Zero Redundancy Optimizer(零冗余优化器):ZeRO-0、ZeRO-1、ZeRO-2、ZeRO-3、ZeRO-Infinity
- ZeRO-Offload :卸载,支持将数据、梯度、优化器状态等下沉到 CPU 和 NVMe
- 自定义混合精度训练训练:动态精度缩放(Dynamic Loss Scaling)和混合精度优化器(Mixed Precision Optimizer)
此外, DeepSpeed 还提供许多大模型相关的工具,如分布式训练管理、内存优化和模型压缩等,以帮助开发者更好地管理和优化大规模深度学习训练任务。
DeepSpeed在自然语言处理(NLP)和多模态等领域有许多成功的应用案例。
DeepSpeed可以极大提升大模型的训练速度、降低训练门槛以及训练成本,并因具备完整健康的社区生态,提升大模型的可用性。让中小公司、独立研究人员解锁了训练具有超过1000亿个参数的模型的能力。
- 参考:LAM
- DeepSpeed is a deep learning optimization library that makes distributed training and inference easy, efficient, and effective.
- DeepSpeed trained the world’s most powerful language models (
MT-530B,BLOOM)
微软的 DeepSpeed 模型并行等内核取自 Megatron ,且 DeepSpeed 主打在数据并行下如何以更少的机器去跑更大的模型 ( ZeRO 、 ZeRO-Offload 等都是用梯度切片、计算、内存/硬盘换入换出来省显存)
目前开源的 模型库 主要是 NVIDIA 的 Megatron-LM 和微软的 DeepSpeed。
Megatron 和 DeepSpeed 都是基于 PyTorch ,分别由 NVIDIA 和微软经过深度定制开发,专门为支持 PyTorch 分布式训练 GPT 而设计的。
NVIDIA 的 Megatron 和 微软的 DeepSpeed:
DeepSpeed 本质是“节省显存”的数据并行,即:数据并行的优化版。
- DeepSpeed 假设了单层参数量在单张显卡上放得下,如果不满足这个假设,那么仍然需要使用
模型并行,而且 DeepSpeed 的模型并行是通过调用 Megatron 来实现的。 - 根据 NVIDIA 论文,
Megatron在大规模训练的效率是超过DeepSpeed不少的。 - DeepSpeed 论文一直强调:用更少机器训练更大的模型,但没有突出过在效率上的优势。
- DeepSpeed 又一篇论文:ZeRO-Infinity,当单层参数量在单张显卡上放不下的时候,它通过对这一层算子切片,一片一片来执行,使得单卡也能跑起来一个巨大的层,可以理解成一种 “时间”轴上展开的模型并行。
DeepSpeed 文档
可视化解读
分布式计算可视化解读
内存开销
- 模型内存:存储模型权重所需的内存。
- 梯度内存:存储每个模型权重梯度所需的内存。
- 优化器内存:存储优化器所需的任何额外状态所需的内存。
- 激活内存:存储在前向传递期间计算的中间值所需的内存。
详见站内专题:GPU显存分析
DeepSpeed 框架
DeepSpeed 分成四个板块,包括:Training、Inference、Compression、Science
DeepSpeed-Training 提供一套端到端大模型训练框架,核心板块。
- 因为 DeepSpeed 基于PyTorch搭建,且兼容 Transformers,新用户学习成本较低,可快速上手,快速实现自有工程的搭建。
- 并且 DeepSpeed 在 DeepSpeedExamples项目中提供了
DeepSpeed-chat模块 ,完美复刻InstructGPT论文中RLHF训练方式,可以一键式完成大模型的SFT、Reward Model Finetuning、RLHF 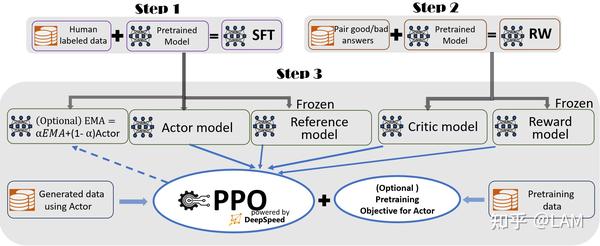
DeepSpeedExamples 也提供 bert、gan、Stable Diffusion 微调案列,更方便的学习应用DeepSpeed。
DeepSpeed发展速度非常快,一些新的大模型热点技术都实现快速支持 。目前DeepSpeed可以支持MoE模型架构训练,并且在超长上下文模型训练问题上也提供了优化方案。
DeepSpeed-Trianing
DeepSpeed-Trianing 介绍
通信策略优化
- 为更好支持GPU、CPU上分布式训练及混合训练。DeepSpeed支持
mpi、gloo和nccl等通信策略 - Open MPI: 整合高性能计算社区中所有专家,技术和资源,以构建可用的最佳MPI库。
Gloo: facebook开源的集体通信库,提供对机器学习中有用的一些集合通信算法如:barrier, broadcast, allreducenccl:NVIDIA集体通信库(NCCL)实现NVIDIA GPU性能优化的多GPU和多节点集体通信原语。NCCL提供了诸如all-gather, all-reduce, broadcast, reduce, reduce-scatter等实现,优化后可以通过PCIe和NVLink等高速互联,高带宽和低延迟。- 因为 NCCL 则是NVIDIA基于自身硬件定制,能做到更有针对性且更方便优化,故在英伟达硬件上,NCCL的效果往往比其它通信库更好。
- 选择策略:
- 如果在 CPU 集群上分布式训练,选择
mpi和gloo; - 如果在 GPU 上进行分布式训练,可以选择
nccl。
- 如果在 CPU 集群上分布式训练,选择
TencentPretrain
- Tencent Pre-training framework in PyTorch & Pre-trained Model Zoo
TencentPretrain 是一个用于对文本、图像、语音等模态数据进行预训练和微调的工具包。
- TencentPretrain遵循模块化的设计原则。通过模块组合,用户能迅速精准的复现已有的预训练模型,并利用已有的接口进一步开发更多的预训练模型。
- 通过TencentPretrain,建立了一个模型仓库,其中包含不同性质的预训练模型(例如基于不同模态、编码器、目标任务)。用户可以根据具体任务的要求,从中选择合适的预训练模型使用。
- TencentPretrain继承了开源项目UER (https://github.com/dbiir/UER-py/) 的部分工作,并在其基础上进一步开发,形成支持多模态的预训练模型框架。
deepspeed 使用
deepspeed 命令
DeepSpeed 官方文档
deepspeed shell
【2024-4-22】将 Python 文件当做 shell 命令
- deepspeed 工具包安装完后,自动增加 shell 命令
deepspeed->/usr/local/bin/deepspeed
- 直接输入 deepspeed 即可启用
deepspeed
# cat /usr/local/bin/deepspeed6
#!/usr/bin/python3
from deepspeed.launcher.runner import main
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
deepspeed ft 流程
模型微调完整流程:
- 数据部分
- 读取tokenizer: 从预训练模型中读取tokenizer
- 读取处理数据 train_dataset, eval_dataset
- 设置 train_sampler, eval_sampler
- 设置 train_dataloader, eval_dataloader (使用DataLoader)
- 模型部分
- 设置DeepSpeed配置参数
- 导入并实例化 model
- 可选:LoRA设置
- 准备需要优化的参数:optimizer_grouped_parameters
- 设置 optimizer
- 设置 lr_scheduler
- 进行初始化 deepspeed.initialize
- 训练及评价部分
- 开始训练 forward,backward,参数更新
- 评价,测试
- 模型保存:
- 注意ZeRO为3时,需要单独处理
启动脚本概要
bash脚本 run_1.3b.sh 调用 main.py 训练,主要学习 main.py 程序。
run_1.3b.sh 脚本主要包含以下内容
deepspeed main.py \
--data_path Dahoas/rm-static \
--data_split 2,4,4 \
--model_name_or_path facebook/opt-1.3b \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--max_seq_len 512 \
--learning_rate 9.65e-6 \
--weight_decay 0.1 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 1 \
--lr_scheduler_type cosine \
--num_warmup_steps 0 \
--seed 1234 \
--zero_stage $ZERO_STAGE \
--deepspeed \
--output_dir $OUTPUT \
&> $OUTPUT/training.log
启动模式
- 单机多卡: 不用 hostfile
- 未指定 hostfile 时, ds 会检测本机可用 GPU 数
- include/exclude 正常使用, 但需要设置 localhost,
deepspeed --include localhost:1 ... CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES控制可用 GPU 失效
- 多机多卡: 要 hostfile 文件, 配合 include/exclude 指定部分节点
- ds 会传播 NCCL and PYTHON 环境变量到各个节点
- 如果想增加变量, 设置 dot 文件
~/.deepspeed_env, 格式NCCL_IB_DISABLE=1; - 如果修改 dot 文件, 修改环境变量
DS_ENV_FILE - mpirun + DeepSpeed 或 AzureML: 安装 mpi4py
deepspeed --hostfile=myhostfile <client_entry.py> <client args> \
--deepspeed --deepspeed_config ds_config.json
启动模式: gpt2/test_tune.sh
MODEL_NAME=gpt2
PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE=1
HF_PATH=~/projects
NEPOCHS=1
NGPUS=16
NNODES=1
MAX_STEPS=200
OUTPUT_DIR=./output_b${PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE}_g${NGPUS}_$MAX_STEPS
TEST=$1
if [ ${TEST} == "0" ]
then
# python -m torch.distributed.launch -> torchrun
torchrun --nproc_per_node=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_0 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
elif [ ${TEST} == "z0" ]
then
deepspeed --num_nodes=$NNODES --num_gpus=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --deepspeed ../dsconfigs/ds_config_fp16_z0.json\
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_z0 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
elif [ ${TEST} == "z1" ]
then
deepspeed --num_nodes=$NNODES --num_gpus=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --deepspeed ../dsconfigs/ds_config_fp16_z1.json\
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_z1 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
elif [ ${TEST} == "z2" ]
then
deepspeed --num_nodes=$NNODES --num_gpus=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --deepspeed ../dsconfigs/ds_config_fp16_z2.json\
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_z2 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
elif [ ${TEST} == "z3" ]
then
deepspeed --num_nodes=$NNODES --num_gpus=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --deepspeed ../dsconfigs/ds_config_fp16_z3.json\
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_z3 \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
elif [ ${TEST} == "tune" ]
then
deepspeed --autotuning run --num_nodes=$NNODES --num_gpus=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --deepspeed ../dsconfigs/ds_config_fp16_tune.json\
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_tune \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
elif [ ${TEST} == "fs" ]
then
torchrun --nproc_per_node=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}_fs \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--save_steps 0 \
--max_steps $MAX_STEPS \
--save_strategy "no"
--sharded_ddp zero_dp_2
fi
启动脚本源码
DeepSpeed/deepspeed/launch 目录下的文件
__init__.py
constants.py
launch.py
launcher_helper.py
multinode_runner.py
runner.py # ds 主入口
from ..autotuning import Autotuner
def run_autotuning(args, active_resources):
# autotune 初始化
tuner = Autotuner(args, active_resources)
logger.info("[Start] Running autotuning")
# tune: 寻参模式
tuner.tune()
tuner.print_tuning_results()
# 保存最优参数
logger.info("[End] Running autotuning")
tuner.write_optimal_config()
# 启动训练任务
if args.autotuning == "run":
tuner.run_after_tuning()
def main(args=None):
args = parse_args(args)
#...
# 当前可用节点信息
active_resources = parse_inclusion_exclusion(resource_pool, args.include, args.exclude)
#...
# 只要 autotuning 非空, 就启用 autotune
if args.autotuning != "":
run_autotuning(args, active_resources)
return
Autotuner 类定义
from .config import DeepSpeedAutotuningConfig
from .constants import *
from .scheduler import ResourceManager
from .tuner import GridSearchTuner, RandomTuner, ModelBasedTuner
from .utils import *
class Autotuner:
"""The DeepSpeed Autotuner automatically discovers the optimal DeepSpeed configuration that delivers good training speed. The Autotuner uses model information, system information, and heuristics to efficiently tune system knobs that affect compute and memory efficiencies, such as ZeRO optimization stages, micro-batch sizes, and many other ZeRO optimization configurations. It not only reduces the time and resources user spend on tuning, but also can discover configurations better than hand-tuned methods.
Autotuning with DeepSpeed requires no code change from DeepSpeed users. Please refer to the README for usage details.
"""
def __init__(self, args, active_resources):
self.args = args
self.selected_exp_dir = None
#...
# 实例化资源管理器 set the active resource for the autotuner resource manager
self.rm = self._get_resource_manager(active_resources)
# 获取实验资源信息:node,gpu数目 get resource requirement for each autotuning experiment
self.exp_num_nodes, self.exp_num_gpus = self._get_exp_resources(args)
def _get_resource_manager(self, active_resources):
"""Initialize and return a resource manager
Args:
active_resources ([dict]): A dictionary of hostname and its slots (GPUs), e.g. {"worker-0": "0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8"}
Raises:
RuntimeError: raises the error if no GPU is available
Returns:
[ResourceManager]: A resource manager that schedules and runs autotuning experiments.
"""
logger.info(f"active_resources = {active_resources}")
hosts = []
ngpus_per_node = 100
# 遍历当前可用主机
for hostname, slots in active_resources.items():
hosts.append(hostname)
ngpus_per_node = min(len(slots), ngpus_per_node)
assert ngpus_per_node > 0, "no gpu is available"
return ResourceManager(args=self.args,
hosts=hosts,
num_gpus_per_node=ngpus_per_node,
results_dir=self.results_dir,
exps_dir=self.exps_dir,
arg_mappings=self.autotuning_config.arg_mappings)
def tune(self): # 参数搜索
""" Tunes Zero stages, micro batch size per GPU, and other Zero configurations. Performance metrics of different tuning spaces are recorded in self.records.
"""
if has_mlflow:
self.mlflow_parent_id = os.environ['MLFLOW_RUN_ID']
mlflow.start_run(run_id=self.mlflow_parent_id)
self.start_time = time.time()
if self.fast_enabled():
logger.info(f"Fast mode is enabled. Tuning micro batch size only.")
# model info profile run with DEFAULT_MIN_MEM_CONFIG
model_info = self.model_info_profile_run()
# ...
def model_info_profile_run(self):
"""Does a model information profiling experiment that collects the number of model parameters and activation memory.\
The experiment produces a "profile_model_info" folder under self.results_dir.
Returns:
[dict]: a model information dictionary, e.g., {"num_params": 335144976, "trainable_num_params": 335144976, "activation_mem_per_gpu": 324358144, "rank": 0}
"""
logger.info("Starting model info profile run.")
model_info = self.autotuning_config.model_info
if model_info and MODEL_INFO_NUM_PARAMS in model_info:
return model_info
ds_config = copy.deepcopy(self.user_config)
replace_dict(ds_config, DEFAULT_MIN_MEM_CONFIG)
model_info_path = os.path.join(self.results_dir, "profile_model_info", "model_info.json")
ds_config[AUTOTUNING] = {"enabled": True, "model_info_path": model_info_path, "model_info": {"profile": True}}
exp_config = {}
exp_name = "profile_model_info"
exp_config['name'] = exp_name
exp_config[DS_CONFIG] = ds_config
exp_config['num_gpus'] = self.exp_num_gpus
exp_config['num_nodes'] = self.exp_num_nodes
exp_config['hostfile'] = self.args.hostfile
exp_path = os.path.join(self.exps_dir, f'{exp_name}.json')
# 读取实验配置信息
with open(exp_path, 'w', buffering=BUFSIZE) as fd:
json.dump(exp_config, fd)
fd.flush()
os.fsync(fd)
# 安排实验任务
self.rm.schedule_experiments([exp_path])
# 启动实验任务: 多线程
self.rm.run()
for exp_id, (exp_json, err) in self.rm.finished_experiments.items():
self.rm.clear()
if err:
logger.error(f"The model is not runnable with DeepSpeed with error = {err}")
return None
if os.path.exists(model_info_path):
with open(model_info_path, 'r') as f:
model_info = hjson.load(f)
return model_info
启动参数
JSON文件 / Dict字典 两种启动传参
- (1)JSON文件
- (2)Dict字典
# (1) Json 文件
deepspeed train.py --deepspeed --deepspeed_config ds_config.json
# (2) 字典
ds_config = {"train_batch_size": 16}
engine, _, _, _ = deepspeed.initialize(model=netconfig=ds_config)
deepspeed train.py --deepspeed
指定GPU运行
# 本机第0张卡
deepspeed --include="localhost:0" train.py --deepspeed --deepspeed_config xxx.jso
DeepSpeed 参数集包括以下内容:
- 1)
–deepspeed:启用 DeepSpeed 的布尔标志 - 2)
–deepspeed_config<json 文件路径>:配置 DeepSpeed 运行时的 json 配置文件的路径。
新增自定义参数
DeepSpeed 使用 argparse 库来为 DeepSpeed 运行时提供命令行配置。
使用 deepspeed.add_config_arguments() 将 DeepSpeed 内置参数添加到应用程序的解析器中。
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='My training script.')
parser.add_argument('--local_rank', type=int, default=-1,help='local rank passed from distributed launcher')
# Include DeepSpeed configuration arguments
parser = deepspeed.add_config_arguments(parser)
cmd_args = parser.parse_args()
参数详解
DeepSpeed分布式启动器各命令含义
| Argument | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
master_port |
主节点端口号 | --master_port 29500 |
master_addr |
主节点ip | --master_addr=10.51.97.28 (ifconfig->eth0->inet) |
nnodes |
节点数 | 两台机器,--nnodes=2 |
node_rank |
节点rank,以第一台机器为0开始递增 | --node_rank=0 master,即主节点rank |
nproc_per_node |
每个节点进程数 | 一个节点使用8张卡,nproc_per_node=8 |
节点通信
NCCL(NVIDIA Collective Communications Library) 参数使用说明
| 参数 | 意义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| NCCL_IB_DISABLE | 禁用IB网卡传输端口 | IB (InfiniBand)是一种用于高性能计算的计算机网络通信标准。 |
| NCCL_SHM_DISABLE | 禁用共享内存传输 | 共享内存(SHM)传输支持运行在相同处理单元/机器中的实体之间的快速通信,这依赖于主机操作系统提供的共享内存机制 |
| NCCL_P2P_DISABLE | 禁用GPU之间信息的传输 | P2P使用CUDA和NVLink直接实现GPU之间的传输与访问 |
关于如何查看GPU是否支持 NVLINK
使用命令
nvidia-smi topo -p2p n #
结果
- V100 上显示结果 (不支持)
- A800 上显示结果 (支持
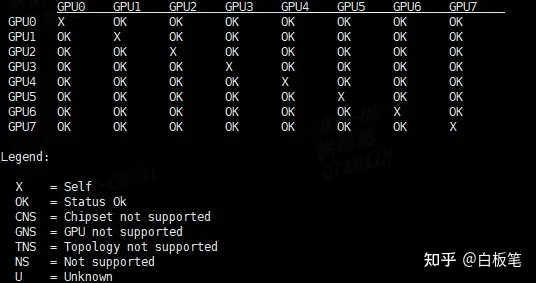
deepspeed 参数
deepspeed 参数列表
usage: deepspeed [-h]
[-H HOSTFILE]
[-i INCLUDE]
[-e EXCLUDE]
[--num_nodes NUM_NODES]
[--min_elastic_nodes MIN_ELASTIC_NODES]
[--max_elastic_nodes MAX_ELASTIC_NODES]
[--num_gpus NUM_GPUS]
[--master_port MASTER_PORT]
[--master_addr MASTER_ADDR]
[--launcher LAUNCHER]
[--launcher_args LAUNCHER_ARGS]
[--module]
[--no_python]
[--no_local_rank]
[--no_ssh_check]
[--force_multi]
[--save_pid]
[--enable_each_rank_log ENABLE_EACH_RANK_LOG]
[--autotuning {tune,run}]
[--elastic_training]
[--bind_cores_to_rank]
[--bind_core_list BIND_CORE_LIST]
[--ssh_port SSH_PORT]
user_script ...
参数含义
deepspeed -h
usage: deepspeed [-h] [-H HOSTFILE] [-i INCLUDE] [-e EXCLUDE] [--num_nodes NUM_NODES] [--min_elastic_nodes MIN_ELASTIC_NODES]
[--max_elastic_nodes MAX_ELASTIC_NODES] [--num_gpus NUM_GPUS] [--master_port MASTER_PORT] [--master_addr MASTER_ADDR]
[--launcher LAUNCHER] [--launcher_args LAUNCHER_ARGS] [--module] [--no_python] [--no_local_rank] [--no_ssh_check]
[--force_multi] [--save_pid] [--enable_each_rank_log ENABLE_EACH_RANK_LOG] [--autotuning {tune,run}]
[--elastic_training] [--bind_cores_to_rank] [--bind_core_list BIND_CORE_LIST] [--ssh_port SSH_PORT]
user_script ...
DeepSpeed runner to help launch distributed multi-node/multi-gpu training jobs.
# 位置参数 positional arguments:
user_script # 要执行的训练脚本入口文件 User script to launch, followed by any required arguments.
user_args # 入口脚本参数
# 可选参数 optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-H HOSTFILE, --hostfile HOSTFILE # 机器资源池
# Hostfile path (in MPI style) that defines the resource pool available to the job (e.g., worker-0 slots=4) (default: /job/hostfile)
-i INCLUDE, --include INCLUDE # 指定可用硬件资源
# Specify hardware resources to use during execution. String format is NODE_SPEC[@NODE_SPEC ...], where NODE_SPEC=NAME[:SLOT[,SLOT ...]]. If :SLOT is omitted, include all slots on that host.
# Example: -i "worker-0@worker-1:0,2" will use all slots on worker-0 and slots [0, 2] on worker-1. (default: )
-e EXCLUDE, --exclude EXCLUDE # 指定不可用的硬件资源
# Specify hardware resources to NOT use during execution. Mutually exclusive with --include. Resource formatting is the same as --include.
# Example: -e "worker-1:0" will use all available resources except slot 0 on worker-1. (default: )
--num_nodes NUM_NODES # 节点总数,使用 hostfile 中 top N 机器
# Total number of worker nodes to run on, this will use the top N hosts from the given hostfile. (default: -1)
--min_elastic_nodes MIN_ELASTIC_NODES # 训练室弹性节点数:最小
# Minimum number of nodes to run elastic training on. Default is 1 when elastic training is enabled (default: -1)
--max_elastic_nodes MAX_ELASTIC_NODES # 训练室弹性节点数:最大
# Maximum number of nodes to run elastic training on. Default is num_nodes when elastic training is enabled (default: -1)
--num_gpus NUM_GPUS, --num_accelerators NUM_GPUS # 每个节点上最多使用的gpu数
# Max number of GPUs to use on each node, will use [0:N) GPU ids on each node. (default: -1)
--master_port MASTER_PORT # 主节点端口,用于分布式训练的通信环节
# (optional) Port used by PyTorch distributed for communication during training. (default: 29500)
--master_addr MASTER_ADDR # 主节点ip地址
# (optional) IP address of node 0, will be inferred via 'hostname -I' if not specified. (default: )
--launcher LAUNCHER # 多机并行方式
# (optional) choose launcher backend for multi-node training. Options currently include PDSH, OpenMPI, MVAPICH, SLURM, MPICH, IMPI. (default: pdsh)
--launcher_args LAUNCHER_ARGS # 多级并行参数
# (optional) pass launcher specific arguments as a single quoted argument. (default: )
--module # Change each process to interpret the launch script as a Python module, executing with the same behavior as 'python -m'. (default: False)
--no_python # 忽略Python脚本,执行执行 Skip prepending the training script with 'python' - just execute it directly. (default: False)
--no_local_rank # 调用用户脚本时忽略local_rank参数 Do not pass local_rank as an argument when calling the user's training script. (default: False)
--no_ssh_check # 不执行ssh验证 Do not perform ssh check in multi-node launcher model (default: False)
--force_multi # 强制多机模式 Force multi-node launcher mode, helps in cases where user wants to launch on single remote node. (default: False)
--save_pid # Save file containing launcher process id (pid) at /tmp/<main-pid>.ds, where <main-pid> is the pid of the first process that invoked `deepspeed`. Useful when launching deepspeed processes programmatically. (default: False)
--enable_each_rank_log ENABLE_EACH_RANK_LOG # 重定向每个节点的标准输出、错误日志
# redirect the stdout and stderr from each rank into different log files (default: None)
--autotuning {tune,run} # 训练前用 autotuner 探索最佳参数, tune 只调参, run 调参后择优运行
# Run DeepSpeed autotuner to discover optimal configuration parameters before running job. (default: )
--elastic_training # 启用弹性训练 Enable elastic training support in DeepSpeed. (default: False)
--bind_cores_to_rank # 绑定 Bind each rank to different cores of the host (default: False)
--bind_core_list BIND_CORE_LIST # 绑定
# List of cores to bind to with comma separated list of numbers and range. i.e. 1,3-5,7 => [1,3,4,5,7]. When not specified, all cores on system would be used rank binding (default: None)
--ssh_port SSH_PORT # ssh端口,用于远程连接 SSH port to use for remote connections (default: None)
hostfile 示例
hostfile.txt
// ip gpu数
10.2.180.1 slots=2
10.2.180.2 slots=2
10.2.180.3 slots=2
超参优化 autotuner
2021年11月15日,DeepSpeed 发布自动化训练策略方案:
- Autotuning 官方文档
- 本质:
- 对 ZeRO stage 和 stage 相对应的ZeRO配置,以及采用梯度累计策略下micro_batch_size大小的自动化搜索。
- 总结:Autotuning 本质是超参数搜索,并没有对数据并行、模型并行的策略进行修改。
- 根据不同超参数配置,自动生成多个实验来计算不同配置下的性能,并从中选择最优的超参数配置。
- 不足:
- Autotuning 显存计算方法跟实现逻辑有区别,且实测 ZeRO3 面临着显存泄露问题,要重新实现模型来规避。
- 显存计算没考虑 torch在cuda初始化时所产生的固定开销。
- 源码参考: Autotuning: 来自DeepSpeed的超参数自动搜索方案
注意:
- DeepSpeed 团队把前向过程产生的中间结果(intermediate results 或feature_maps或intermediate activation)叫做激活值(activation)
- ZeRO stages, micro-batch sizes 和其他配置可被用户配置覆盖。
Autotuning 流程
- (1) Autotuner 先做 profile 工作,分析所需运行模型的参数量以及激活值的内存。 即跑一遍前向然后结束进程
Autotuner.model_info_profile_run()起一个小experiment, 获取参数量和激活值大小ResourceManager.run()调用self.run_job(exp, reservations),其中reservations为可用GPU设备信息。ResourceManager.run_job(exp, reservations)启动线程(thread)运行run_experiment函数run_experiment(exp, reservations, user_script, user_args)利用subprocess库执行cmd命令- 示例:
deepspeed --force_multi --include localhost:2 --master_port 12345 my_model_train.py --ds_config_path ds_config.json
- 示例:
- (2) Autotuner 以
[0, 1, 2, 3]顺序先搜索 ZeRO stage,估计每个GPU在训练模型时所需的最小memory(ZeRO实例化时所需的显存量),并与当前GPU可用显存进行比较。如果小于GPU可用显存,则说明该stage可以运行。Autotuner 尝试搜索该stage下每个GPU的micro-batch的大小,以及其他的ZeRO设置: - (3) 如果当前 ZeRO stage 最优设置性能亚于之前其他ZeRO stage的方法,则之后其他Stage的搜索会终止。(因为是按顺序搜索的,默认情况下,前面的stage的最优策略应该batch-size会更小)
- (4) 最后,全局最优设置会通过log的文件的形式告知用户。如果
--autotune设置为run,还会直接开始训练。
支持: 随机/网格/模型搜索
exps = self._generate_experiments(tuning_space, max_train_batch_size_per_gpu)
logger.info(f'Tuner type is {self.autotuning_config.tuner_type}')
if self.autotuning_config.tuner_type == AUTOTUNING_TUNER_MODELBASED:
t = ModelBasedTuner(exps, self.rm, self.metric(), tuning_space)
elif self.autotuning_config.tuner_type == AUTOTUNING_TUNER_RANDOM:
t = RandomTuner(exps, self.rm, self.metric())
else:
t = GridSearchTuner(exps, self.rm, self.metric())
sample_size = len(self.rm.nodes) * self.rm.num_gpus_per_node // (self.exp_num_gpus * self.exp_num_nodes)
num_exps = t.tune(sample_size=sample_size,
n_trials=self.autotuning_config.tuner_num_trials,
early_stopping=self.autotuning_config.tuner_early_stopping)
exp = t.best_exp
metric_val = t.best_metric_val
官方示例 GPT-2 实践
使用方法
- 增加配置文件
ds_config.json, 开启自动寻参功能"autotuning": {"enabled": true},arg_mappings中指定个别参数映射关系 - 启动脚本
test_tune.sh- deepspeed 命令行中增加参数:
--autotuning run/tune
- deepspeed 命令行中增加参数:
ds_config.json 文件
{
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"fp16": {
"enabled": true
},
"autotuning": {
"enabled": true,
"arg_mappings": {
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "--per_device_train_batch_size",
"gradient_accumulation_steps ": "--gradient_accumulation_steps"
}
}
}
训练脚本
- transformers 提供的pytorch模型源码 examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py
- DeepSpeedExamples 训练脚本 test_tune.sh
- 支持多种模式:
0(torchrun分布式),z1,z2,z3,tune(ds 自动寻参训练),fs
- 支持多种模式:
deepspeed --autotuning run --num_nodes=$NNODES --num_gpus=$NGPUS $HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --deepspeed $DS_CONFIG\
--model_name_or_path $MODEL_NAME \
--dataset_name wikitext \
--dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--fp16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE \
--gradient_accumulation_steps $GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEPS \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs $NEPOCHS \
--output_dir ${OUTPUT_DIR} \
--overwrite_output_dir
踩坑:
- test_tune.sh
- 更新 example示例代码里的 HF_PATH
python -m torch.distributed.launch->torchrun
- cannot import name ‘is_torch_xla_available’ from ‘transformers’
- 编辑
$HF_PATH/transformers/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py59 行, 注释check_min_version("4.41.0.dev0"), 不做版本要求
- 编辑
# 环境准备
# transformers (4.12.0.dev0)
pip install transformers -U # 并关闭 59行版本检测, 否则 cannot import name 'is_torch_xla_available' from 'transformers
# datasets (1.11.0)
pip install datasets # 否则 ConnectionError: Couldn't reach 'wikitext' on the Hub (ConnectTimeout)
# (1) transformers 版本问题: 4.38 -> 4.40, 关闭 59行版本检测
# cannot import name 'is_torch_xla_available' from 'transformers
# (2) shell if 判断报错: zsh -> bash
sh test_tune.sh tune # if [] 判断语法错误
bash test_tune.sh tune # 改成 bash
# (3)
# [ERROR] [autotuner.py:700:model_info_profile_run] The model is not runnable with DeepSpeed with error = No module named 'evaluate'
bash test_tune_wqw.sh tune
main.py 参数
usage: main.py [-h] [--data_path [DATA_PATH ...]] [--data_split DATA_SPLIT] [--data_output_path DATA_OUTPUT_PATH] [--model_name_or_path MODEL_NAME_OR_PATH]
[--num_padding_at_beginning NUM_PADDING_AT_BEGINNING]
[--per_device_train_batch_size PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE]
[--per_device_eval_batch_size PER_DEVICE_EVAL_BATCH_SIZE]
[--max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN]
[--learning_rate LEARNING_RATE]
[--minimum_learning_rate MINIMUM_LEARNING_RATE]
[--weight_decay WEIGHT_DECAY]
[--num_train_epochs NUM_TRAIN_EPOCHS]
[--gradient_accumulation_steps GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEPS]
[--lr_scheduler_type {linear,cosine,cosine_with_restarts,polynomial,constant,constant_with_warmup}]
[--num_warmup_steps NUM_WARMUP_STEPS]
[--class_weight CLASS_WEIGHT]
[--device DEVICE]
[--output_dir OUTPUT_DIR]
[--seed SEED]
[--gradient_checkpointing]
[--dropout DROPOUT]
[--offload]
[--dtype {fp16,bf16}]
[--zero_stage ZERO_STAGE]
[--lora_dim LORA_DIM]
[--lora_module_name LORA_MODULE_NAME]
[--only_optimize_lora]
[--lora_learning_rate LORA_LEARNING_RATE]
[--eval_interval EVAL_INTERVAL]
[--eval_iters EVAL_ITERS]
[--print_steps PRINT_STEPS]
[--save_steps SAVE_STEPS]
[--compute_fp32_loss]
[--enable_tensorboard]
[--tensorboard_path TENSORBOARD_PATH]
[--add_eot_token]
[--im_start IM_START]
[--im_end IM_END]
[--system SYSTEM]
[--user USER]
[--assistant ASSISTANT]
[--train_data_path TRAIN_DATA_PATH]
[--val_data_path VAL_DATA_PATH]
[--test_data_path TEST_DATA_PATH]
[--inference]
[--restore]
[--checkpoint CHECKPOINT]
[--debug]
[--model_name MODEL_NAME]
[--template TEMPLATE]
[--label1_dim LABEL1_DIM]
[--label2_dim LABEL2_DIM]
[--label3_dim LABEL3_DIM]
[--chinese_percent CHINESE_PERCENT]
[--only_query]
[--cut_flag_token CUT_FLAG_TOKEN]
[--cut_flag_token_id CUT_FLAG_TOKEN_ID]
[--deepspeed]
[--deepspeed_config DEEPSPEED_CONFIG]
[--deepscale]
[--deepscale_config DEEPSCALE_CONFIG]
[--deepspeed_mpi]
结合 main.py 程序,将参数分为三大类
| 参数 | 类型 | 含义 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
data_path |
数据 | huggingface数据路径 | Dahoas/rm-static |
data_split |
数据 | 3个阶段数据拆分方式 | 2,4,4 是 step1,2,3 分配的数据比例 |
max_seq_len |
数据 | 最大序列长度(超过长度会阶段) | |
data_output_path |
数据 | 输出数据本地路径 | |
model_name_or_path |
模型 | 模型名称/路径,可以是hf | facebook/opt-1.3b |
lora_dim |
模型 | 如果大于0,则用LoRA优化 | |
lora_module_name |
模型 | 设置LoRA范围 | 可只针对 decoder.layers |
only_optimize_lora |
模型 | 是否只优化LoRA | |
per_device_train_batch_size |
训练 | 训练时每个GPU的Batch Size | |
per_device_eval_batch_size |
训练 | 评价时每个GPU的Batch Size | |
learning_rate |
训练 | 学习率 | |
weight_decay |
训练 | 权重衰减,防止过拟合 | |
num_train_epochs |
训练 | 训练 epoch 数 | |
gradient_accumulation_steps |
训练 | 梯度更新步数 | |
lr_scheduler_type |
训练 | learning rate的调整策略 | linear, cosine |
zero_stage |
deepspeed | DeepSpeed工具中的zero方式 | 0,1,2,3 |
offload |
deepspeed | ZeRO-Offload利用CPU资源辅助降低GPU计算和内存需求 | |
local_rank |
deepspeed | 标识当前 GPU 设备的本地排名(本机排名,与global-rank不同) | |
gradient_checkpointing |
deepspeed | 降低训练中的内存消耗 | |
seed |
其它 | 随机排序种子 | |
output_dir |
其它 | 模型存储目录 | |
官方文档: DeepSpeed Configuration JSON
数据源
数据相关
data_path : 数据路径,huggingface数据, 比如:Dahoas/rm-static
data_split : 数据的拆分方式,比如 2,4,4 是为step1,2,3分配的数据比例
max_seq_len : 最大序列长度(超过长度会被截掉)
data_output_path : 相关数据的存储地址(local storage,不能是shared storage)
模型
模型相关
model_name_or_path : 模型名称或路径,huggingface模型,比如:facebook/opt-1.3b
lora_dim : 如果大于0,则使用LoRA优化
lora_module_name : 设置LoRA的范围,比如可以只针对 decoder.layers
only_optimize_lora : 是否只优化LoRA的参数
训练
训练相关
per_device_train_batch_size : 训练时的 Batch size (per device: 每个GPU的Size)
per_device_eval_batch_size : 评价时的 Batch size (per device)
learning_rate : 学习率
weight_decay : 权重衰减,防止模型过拟合的技术。
num_train_epochs : 训练 epoch 数
gradient_accumulation_steps : 累积多少个 mini-batch 的梯度后再进行一次参数更新。
lr_scheduler_type : learning rate的调整策略,比如 linear, cosine
注意:
train_batch_size=train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu*gradient_accumulation_steps*number of GPUs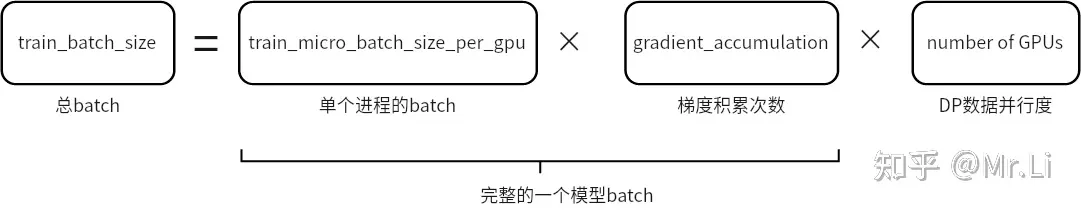
train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu是单个GPU上前向、反向的实际 batch_sizegradient_accumulation_steps是梯度累积步数- 指定其中2个参数, 最后1个参数可由 deepspeed 自动推导
{
"train_batch_size": 16, //总batch
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": 8,
"gradient_accumulation": 1
} //2个GPU
可视化监控
支持多种可视化监控
- PyTorch’s TensorBoard, WandB, and simple CSV files
开启TensorBoard可视化
"tensorboard": {
"enabled": true, //开启可视化
"output_path": "log/", //可视化文件保存路径
"job_name": "2023年08月15日16:28:06" //此次实验名称,作为子文件夹
}
//========================
{
"tensorboard": {
"enabled": true,
"output_path": "output/ds_logs/",
"job_name": "train_bert"
}
"wandb": {
"enabled": true,
"team": "my_team",
"group": "my_group",
"project": "my_project"
}
"csv_monitor": {
"enabled": true,
"output_path": "output/ds_logs/",
"job_name": "train_bert"
}
}
deepspeed
deepspeed 相关
zero_stage : 这个对应者DeepSpeed工具中的zero方式,分别是0,1,2,3
offload : ZeRO-Offload 通过利用主机CPU上的计算和内存资源来执行优化器,从而减少此类模型的GPU计算和内存需求。
local_rank : 分布式训练时的一个变量,用于标识当前 GPU 设备的本地排名(本机排名,与global-rank不同)
gradient_checkpointing : 降低深度学习模型训练过程中内存消耗的技术
deepspeed 核心参数
__init__.py文件中已定义, 不能重复定义,否则报错
deepspeed : deepspeed 开关, 对后端无影响
deepspeed_config : deepspeed 配置文件 json 格式
deepscale : deepspeed 开关, 废弃的 '旧版deepspeed'
deepscale_config : deepspeed 配置文件 json 格式('旧版deepspeed_config')
deepspeed_mpi: 启用 MPI 模式(CPU 并行)
其他
seed : 随机排序是的seed
output_dir : 模型的存储目录
分布式参数
args.local_rank
local_rank是分布式训练时变量,标识当前 GPU 设备的本地排名(local rank)。args.local_rank = -1,表示代码不在分布式设置下运行,仅使用单个 GPU 训练。args.local_rank ≠ -1,代码在分布式设置下运行,当前 GPU 设备被分配了一个唯一的本地排名。- 代码会将设备设置为指定的 GPU(
torch.device("cuda", args.local_rank)),并使用deepspeed.init_distributed()函数调用初始化分布式后端。
- 代码会将设备设置为指定的 GPU(
注意:
- PyTorch 中也有分布式初始化方法
torch.distributed.init_process_group()函数。 - 但是当使用 DeepSpeed 库时,不要替换为
deepspeed.init_distributed()。
args.global_rank
- 分布式训练中,每个进程都有唯一的全局排名,用于标识该进程在分布式环境中的位置。
- 全局排名的范围:
0 ~ world_size-1,其中world_size是整个分布式环境中进程总数。 - 本程序中通过
torch.distributed.get_rank()来读取global_rank, 本函数在初始化分布式后端之后才能调用。
torch.distributed.barrier()
- torch.distributed.barrier() 是同步函数,用于分布式环境中同步各个进程的状态。
- 调用该函数时,进程会阻塞等待,直到所有进程都调用了该函数之后,才会解除阻塞并继续执行后面的代码。
分布式训练中,torch.distributed.barrier() 通常用于同步各个进程的梯度更新。
- 每个进程完成一轮前向传播和反向传播后,要同步各自的梯度,并且等待其他进程完成同样的操作,才能进行下一轮更新。
- 这时用 torch.distributed.barrier() 函数实现同步。
另外一个用法,在模型参数并行训练时,数据的读取只需要在 local_rank 为 0 的GPU上进行,其他进程使用 torch.distributed.barrier() 来阻塞来等待数据读取完成。
指定GPU运行
# 本机第0张卡
deepspeed --include="localhost:0" train.py --deepspeed --deepspeed_config xxx.json
数据处理
分词
DS-Chat 使用的 tokenizer 来自预训练模型
- Hugging Face Transformers 库中的 AutoTokenizer 类实例化预训练模型的 tokenizer。
- AutoTokenizer 类自动选择并加载对应的 tokenizer,避免了手动选择的步骤。
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path, fast_tokenizer=True)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained() 函数有两个必选参数
model_name_or_path预训练模型的名称或路径,例如: “bert-base-uncased” 或 “/path/to/model/directory”。fast_tokenizer: 是否用快速 tokenizer。- 如果为 True,则会选择使用 Rust 实现的 tokenizer,速度更快;
- 否则使用 Python 实现的 tokenizer。默认为 True。
数据准备
数据准备函数: create_prompt_dataset
train_phase = 1
train_dataset, eval_dataset = create_prompt_dataset(
args.local_rank, args.data_path, args.data_split,
args.data_output_path, train_phase, args.seed, tokenizer,
args.max_seq_len)
说明
local_rank数据下载等基本处理只在local rank为 0 的 GPU 上执行。每个node上只处理一次数据即可。 -data_output_path设定为 local storage path,分布式训练时存储本地数据用的。
初始化sampler
- 单GPU 用RandomSampler和SequentialSampler
- 分布式处理使用DistributedSampler。
sampler 主要用来设置数据采样顺序。
- 比如随机采样来提高模型的鲁棒性。
# DataLoaders creation:
if args.local_rank == -1:
train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_dataset)
eval_sampler = SequentialSampler(eval_dataset)
else:
train_sampler = DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
eval_sampler = DistributedSampler(eval_dataset)
数据读取使用 PyTorch 标准的 DataLoader 来处理。
- Dataloader 不仅可以设置sampler定义采样方式,还可以自动进行批处理,并且支持多进程数据加载。
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset,
collate_fn=default_data_collator,
sampler=train_sampler,
batch_size=args.per_device_train_batch_size)
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset,
collate_fn=default_data_collator,
sampler=eval_sampler,
batch_size=args.per_device_eval_batch_size)
模型
计算模型显存
计算 Transformer 模型内存需求的脚本:distributed-training-and-deepspeed/estimate_transformer_memory.py
模型初始化
(1) 模型初始化
对模型进行初始化。
model = create_hf_model(AutoModelForCausalLM, args.model_name_or_path,
tokenizer, ds_config)
其中 AutoModelForCausalLM 是 Hugging Face Transformers 库中的一个类,能够自动选择并加载适当的预训练 Transformer 模型,它支持多种预训练 Transformer 模型,包括 GPT-2、GPT、CTRL、Transformer-XL、XLNet 和 XLM 等。使用该类时,您只需指定模型的名称或路径即可自动加载对应的模型。
具体实现代码,可以参考:utils/model/model_utils.py。
LoRA
(2) LoRA
LoRA
- 当lora_dim>0时,用LoRA技术对模型进行调整。 从而让模型的优化参数大幅度的变少,改善优化的效率。
通常使用LoRA技术,不仅可以减少参数量,还能进一步改善性能。
因为,这种bottleneck的网络设计,可以防止过拟合,提高模型的鲁棒性。
if args.lora_dim > 0:
model = convert_linear_layer_to_lora(model, args.lora_module_name, args.lora_dim)
if args.only_optimize_lora:
model = only_optimize_lora_parameters(model)
提取需要被优化的参数 optimizer_grouped_parameters
# Split weights in two groups, one with weight decay and the other not.
optimizer_grouped_parameters = get_optimizer_grouped_parameters(
model, args.weight_decay)
AdamOptimizer = DeepSpeedCPUAdam if args.offload else FusedAdam
optimizer = AdamOptimizer(optimizer_grouped_parameters,
lr=args.learning_rate,
betas=(0.9, 0.95))
上面代码中,get_optimizer_grouped_parameters() 函数被用来将权重分成两组,一组需要应用权重衰减,另一组则不需要。该函数通过遍历模型的所有参数,并检查参数名称是否包含 bias 或 LayerNorm 等特殊字符串,来区分需要应用权重衰减的参数和不需要的参数。
分组原因:
- 对于参数名称中不包含 bias 或 LayerNorm 等特殊字符串的参数,我们认为它们是需要应用权重衰减的参数。对于这些参数,通常会将它们的权重矩阵与权重衰减超参数相乘,以降低它们的权重。与此相反,对于参数名称中包含 bias 或 LayerNorm 等特殊字符串的参数,我们认为它们是不需要应用权重衰减的参数。这是因为 bias 或 LayerNorm 参数通常只是用来偏移或缩放其他层的输出,而不是真正的权重参数。通过将权重分成两组,并分别应用权重衰减和不应用权重衰减,我们可以更好地控制模型的复杂度,从而提高模型的泛化性能。
然后设置Optimizer优化器,根据参数不同会选择 DeepSpeedCPUAdam 或者 FusedAdam 优化器。 并传入了一些参数,包括分组的参数、学习率和 betas。
Adam优化器:
- 在 Hugging Face 的 Transformers 库中,有两种 Adam 优化器可供选择:FusedAdam 和 DeepSpeedCPUAdam。它们都是基于 PyTorch 实现的优化器,但在不同的硬件上具有不同的优化和性能特征。FusedAdam 是使用 NVIDIA Apex 库实现的优化器,它支持混合精度训练,并且可以同时计算梯度和权重更新操作,从而提高训练效率。FusedAdam 优化器在使用支持 CUDA 的 NVIDIA GPU 时具有较好的性能。DeepSpeedCPUAdam 是一种 CPU 上的优化器,它是 DeepSpeed 框架中的一部分,支持分布式训练和模型平行化。DeepSpeedCPUAdam 优化器在使用 CPU 时具有较好的性能。在上面的代码中,如果 args.offload 为 True,则表示使用基于 CPU 的优化,因此会选择使用 DeepSpeedCPUAdam 优化器。
lr_scheduler
(3) 设置 lr_scheduler
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(
len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
name=args.lr_scheduler_type,
optimizer=optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=args.num_warmup_steps,
num_training_steps=args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch,
)
lr_scheduler 是用来规划整个训练过程中 lr 是如何调整的。lr_scheduler_type 调度器类型,用来描述 lr 是按照什么样的方式变化,例如 LinearWarmup、CosineAnnealing 等。num_warmup_steps 预热步数指定了在训练的前期阶段 lr 增加过程的步数。 总训练步数指定模型共被更新多少次。
DS初始化
model, optimizer, _, lr_scheduler = deepspeed.initialize(
model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
args=args,
config=ds_config,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
dist_init_required=True)
使用DeepSpeed进行优化是,需要使用deepspeed.initialize() 函数来初始化模型、优化器、学习率调度器等训练相关的组件。其中,model 和 optimizer 是必需的参数,而其他参数则是可选的。
deepspeed.initialize() 函数会对传入的参数进行检查和优化,并返回新的模型、优化器和学习率调度器等组件。例如,它会根据训练参数设置和硬件配置自动调整优化器和梯度累积的设置,并设置模型权重的分布式训练策略。dist_init_required=True 参数指示 DeepSpeed 是否需要进行分布式训练初始化。
DS 配置文件
- 配置文件包含DeepSpeed模型训练时所需要的相关设置信息,可以通过这里的修改来调整训练过程。
下面是 utils/ds_utils.py 中设置 :
ds_config = {
"train_batch_size": GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE,
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": MICRO_BATCH_SIZE,
"steps_per_print": 10,
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": stage,
"offload_param": {
"device": device
},
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": device
},
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 1e4,
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 3e7,
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 3e7,
"memory_efficient_linear": False
},
"fp16": {
"enabled": True,
"loss_scale_window": 100
},
"gradient_clipping": 1.0,
"prescale_gradients": False,
"wall_clock_breakdown": False,
"hybrid_engine": {
"enabled": enable_hybrid_engine,
"inference_tp_size": inference_tp_size,
"release_inference_cache": release_inference_cache,
"pin_parameters": pin_parameters,
"tp_gather_partition_size": tp_gather_partition_size,
}
}
训练部分的实现代码
- 使用DS以后,训练部分的代码与标准的PyTorch代码不同。
for epoch in range(args.num_train_epochs):
print_rank_0(
f"Beginning of Epoch {epoch+1}/{args.num_train_epochs}, Total Micro Batches {len(train_dataloader)}",
args.global_rank)
model.train()
for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
batch = to_device(batch, device)
outputs = model(**batch, use_cache=False)
loss = outputs.loss
model.backward(loss)
model.step()
**batch解释:
-
**batch将一个批次的数据传递给模型,避免手动拆分列表或元组,使代码更加简洁易读。
*batch表示将一个列表对象 batch 中的元素拆分成独立的参数传递给函数或方法。- 例如:
*batch = (input_ids, attention_mask, labels) - 用 *batch 时,等价于将这些 Tensor 对象拆分为独立的参数,即:
model(*batch)等价于model(input_ids, attention_mask, labels)
- 例如:
**batch将一个字典对象 batch 拆分成独立的参数传递给函数或方法。- 例如:
batch = {'input_ids': input_ids, 'attention_mask': attention_mask, 'labels': labels} model(**batch)等价于model(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, labels=labels)
- 例如:
评价
通过 perplexity 来对模型进行评价。
# Evaluate perplexity on the validation set
perplexity = evaluation(model, eval_dataloader)
模型保存
if args.output_dir is not None:
print_rank_0('saving the final model ...', args.global_rank)
model = convert_lora_to_linear_layer(model)
if args.global_rank == 0:
save_hf_format(model, tokenizer, args)
if args.zero_stage == 3:
# For zero stage 3, each gpu only has a part of the model, so we need a special save function
save_zero_three_model(model,
args.global_rank,
args.output_dir,
zero_stage=args.zero_stage)
DeepSpeed 实例
AlexNet 训练
以 alexnet 为例, 体验 deepspeed 训练, github 文件: pipeline_parallelism
deepspeed train.py --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json -p 2 --steps=200
{
"train_batch_size" : 256,
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu" : 8,
"optimizer": {
"type": "Adam",
"params": {
"lr": 0.001,
"betas": [
0.9,
0.999
],
"eps": 1e-8
}
},
"steps_per_print" : 10,
"wall_clock_breakdown" : false
}
单机单卡实验
- A100 训练200步完毕
DeepSpeed-Chat
DeepSpeed 是 Microsoft基于 PyTorch 研发的开源深度学习优化库。
- 目的: 降低大模型训练的门槛,提升大模型的训练的效率,帮助开发者更有效率地管理及优化大模型的训练、部署任务。
DSChat代码解读
- 【2024-3-29】大模型训练入门实战
- 【2024-8-18】从零实现带RLHF的类ChatGPT:逐行解析微软DeepSpeed Chat的源码
DeepSpeed-Chat 介绍
DeepSpeed-Chat 微软发布的类ChatGPT模型训练工具。
- 基于微软的大模型训练工具DeepSpeed,简单高效地训练ChatGPT。
工具特点:
- 类ChatGPT完整训练代码:包括 预训练模型下载、数据下载、InstructGPT 训练过程和测试。
- 多规模模型:模型参数从1.3B到66B,适合新手学习, 可商用部署。
- 高效训练:通过使用最新技术(
ZeRO和LoRA等)改善训练过程。- 例如,一个67亿(6.7B)参数的模型,使用8块A00只需要约5个小时完成训练。
- 推理API:提供易于使用的推理API,方便对话式交互测试。
视频讲解
DeepSpeed-Chat 部署
推荐设置:
- Linux 操作系统
- GPU 24G 以上显存
- CUDA 版本 11.7
# conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=11.7 -c pytorch -c nvidia
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeedExamples.git
cd DeepSpeedExamples/applications/DeepSpeed-Chat/
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
DeepSpeed-Chat 代码
DS-chat 代码位于 applications/DeepSpeed-Chat 目录下,主要程序结构:
train.py# 入口程序- training # 训练脚本
- step1_supervised_finetuning # 第1步训练
- evaluation_scripts # 第1步训练后,评价
- training_scripts # 模型训练脚本
- README.md # 说明文档
main.py# 主程序,训练过程的实现细节prompt_eval.py# 评价主程序
- step2_reward_model_finetuning # 第二步训练
- 省略
- step3_rlhf_finetuning # 第三步训练
- 省略
- utils 模型训练,评价的相关函数库
- step1_supervised_finetuning # 第1步训练
- inference # 测试,评价代码
模型训练调用过程(以1.3b模型为例)
deepspeed 总入口在 deepspeed.__init__::initialize
实践
deepspeed chat 框架
目录结构
dschat/ # 核心目录
rlhf/ # RLHF算法
ppo_trainer.py
rlhf_engine.py
utils/
data/
data_utils.py # 【数据处理入口】【自定义】sft 数据处理类
reward_datasets.py # 【自定义】rm 数据处理
model/ # 模型配置、定义
model_utils.py
quantization.py
reward_model.py
# LLM 个性化信息, chatglm,qwen,internlm等
configuration_internlm2.py # internlm 配置
modeling_internlm2.py # internlm 结构, 头部引入以上配置文件,
# from .configuration_internlm2 import InternLM2Config
module/ # 组件, 如 lora
lora.py
ds_utils.py
optimization.py
perf.py
utils.py
inference/
tests/
tranining/
step1_supervised_finetuning/
step2_reward_model_finetuning/
step3_rlhf_finetuning/
conversation_reward/ # 【自定义】监督学习训练任务
main.py
run.sh
run.sh
debug.sh
e2e_rlhf.py
requirements.xt
to_onnx.py
改进点
- 数据处理
- 数据格式: 兼容多种数据格式
- LLM 相关: 特殊分隔符
<sos>,<eos>,UNK, padding 策略, 转 chatml 格式 - 任务格式: 支持二分类、多分类, num_classes = 2, 11
- 会话数据格式转换:
- 只保留q:
[q1,a1,q2,a2]->[q1,q2] - 保留qa,截断: 按最近窗口截断
- 只保留q:
- 数据不均衡
- 数据集再均衡: 降采样
- loss 改进: focal loss/ class balanced loss
- 训练监控
- 增加 wandb: 训练参数变化可视化
- 训练模式
- 单机多卡: GPU 显存预估
- 分布式: torch.distribute 开启分布式模式, dist.
all_gather(labels1_all_gather, labels_all1)
- 调参
- 学习率: batch_size, learning_rate (衰减策略)
- 自动调参: autotune
- 模型保存
- 模型自动保存: 不再是每个epoch保存模型, 而是 loss 取值下滑/acc指标上升 才保存模型
- 转 onnx 格式: onnxruntime 推理加速
- 效果评估
- 可视化: 验证集指标输出, 混淆矩阵 -> 可视化
- 推理预测
- inference.py 中需要单独处理 model 修改部分
# 超参
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='reward model for AI charactor')
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='stransformers', help='choose a model: bert, ERNIE, bert_CNN')
parser.add_argument('--local_rank')
parser.add_argument('--model_name', type=str, default='stransformers')
parser.add_argument('--data_map', type=str, help="数据格式字段映射关系",
default='{"prompt":"prompt","label":"label_id", "history":"context_info"}')
# 推理环节
def main():
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 模型加载
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.model_path)
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.model_path)
tokenizer.truncation_side = "right" # 默认是right
tokenizer.padding_side = "right" # 默认是right
# 加载数据集
_, _, test_data = build_dataset(args, tokenizer) # python list
test_data = RewardDataset(test_data) # pytorch datasets 格式
# pytorch tensor 格式, torch.LongTensor
test_iter = Data.DataLoader(dataset=test_data, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True)
model = Model(args)
# 设备适配: cpu, gpu
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
else:
state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path)
if not args.inference: # 训练模式
model = Model(args)
logging.info("load model finished")
if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
logging.info('Let us use ' + str(torch.cuda.device_count()) + "GPUs!")
model = nn.DataParallel(model)
model = model.to(device)
# train
train(args, model, train_iter, dev_iter, test_iter, device, logging)
else: # 推理模式
# 模型权重
state_dict_new = {}
for key,value in state_dict.items():
if key.startswith("module"): # 模型自定义参数
new_key = key.lstrip("module")[1:]
else: # 默认参数
new_key = key
# 存储到字典
state_dict_new[new_key] = value
model.load_state_dict(state_dict_new)
if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
print('Let us use ' + str(torch.cuda.device_count()) + "GPUs!")
model = nn.DataParallel(model)
model = model.to(device)
test_en_acc1, test_en_acc2, predict_tag_list, acc1_list, acc2_list, indexs_all = evaluate(model, test_en_iter, label2tag_dic, device=device)
test_en = pd.merge(test_en, pd.DataFrame({"index": indexs_all, "predict": predict_tag_list, "acc1": acc1_list, "acc2": acc2_list}), on="index", how="inner")
print(f"en, acc1: {test_en_acc1}, acc2: {test_en_acc2}")
def train(args, model, train_iter, dev_iter, test_iter, device, logging):
model.train()
# param_optimizer = list(model.named_parameters())
# no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']
# optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
# {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.01},
# {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.0}]
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
# optimizer = BertAdam(optimizer_grouped_parameters,
# lr=config.learning_rate,
# warmup=0.05,
# t_total=len(train_iter) * config.num_epochs)
total_batch = 0 # 记录进行到多少batch
dev_best_acc = -float('inf')
last_improve = 0 # 记录上次验证集loss下降的batch数
flag = False # 记录是否很久没有效果提升
model.train()
if args.loss_type == "focal_loss":
loss_functioin = FocalLoss(alpha=args.alpha)
else:
#class_weight = torch.tensor([float(x) for x in args.class_weight.split(",")]).to(device)
#loss_functioin = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=class_weight)
loss_functioin = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(args.num_epochs):
logging.info('Epoch [{}/{}]'.format(epoch + 1, args.num_epochs))
for i, (x, seq_len, mask, labels, _) in enumerate(train_iter):
trains = (x.to(device), seq_len, mask.to(device))
labels = labels[:,0].to(device)
outputs = model(trains) # trains[0].shape [batch_size, dim], trains[1].shape [batch_size], trains[2].shape [64, 512]
model.zero_grad()
loss = loss_functioin(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if total_batch % args.loss_print_every_n_iter == 0:
# 每多少轮输出在训练集和验证集上的效果
true = labels.data.cpu()
predic = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)[1].cpu()
train_acc = metrics.accuracy_score(true, predic)
dev_acc, dev_auc, *_ = evaluate(model, dev_iter)
test_acc, test_auc, *_ = evaluate(model, test_iter)
if dev_acc > dev_best_acc:
dev_best_acc = dev_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), args.save_path)
improve = '*'
last_improve = total_batch
else:
improve = ''
msg = 'Iter: {0:>6}, Train Loss: {1:>5.2}, Train Acc: {2:>6.2%}, dev Acc: {3:>6.2%}, dev auc: {4:>6.2%}, test Acc: {5:>6.2%}, test auc: {6:>6.2%}, {7}'
logging.info(msg.format(total_batch, loss.item(), train_acc, dev_acc, dev_auc, test_acc, test_auc, improve))
model.train()
total_batch += 1
if total_batch - last_improve > args.require_improvement:
# 验证集loss超过1000batch没下降,结束训练
logging.info("No optimization for a long time, auto-stopping...")
flag = True
break
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(args.save, 'checkpoint-' + 'epoch-' + str(epoch + 1) + '.pth'))
if flag:
break
# epoch结束测试一次
test(args, model, test_iter, logging)
model.train()
def evaluate(model, data_iter, device=torch.device('cuda')):
model.eval()
loss_total = 0
predict_all = np.array([], dtype=int)
labels_all = np.array([], dtype=int)
indexs_all = np.array([], dtype=int)
score_all = np.array([], dtype=float)
loss_functioin = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (x, seq_len, mask, labels, indexs) in enumerate(data_iter):
trains = (x.to(device), seq_len, mask.to(device))
labels = labels.to(device)[:,0]
outputs = model(trains)
outputs_score = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
loss = loss_functioin(outputs, labels)
loss_total += loss
# 按照thresholds来计算新的label
predic = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)[1]
predic = predic.cpu().numpy()
labels = labels.data.cpu().numpy()
indexs_all = np.append(indexs_all, indexs.numpy())
predict_all = np.append(predict_all, predic)
labels_all = np.append(labels_all, labels)
score_all = np.append(score_all, outputs_score.cpu().numpy()[:, 1])
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(labels_all, score_all, pos_label=1)
auc = round(metrics.auc(fpr, tpr), 4)
accuracy = round(metrics.accuracy_score(labels_all, predict_all), 4)
confusion_matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(labels_all, predict_all)
classification_report = metrics.classification_report(labels_all, predict_all)
# 计算准确率
return accuracy, auc, confusion_matrix, classification_report, indexs_all
run.sh
#!/usr/bin/bash
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
# **************************************************************************
# * Copyright (c) 2024 wqw547243068@163.com, All Rights Reserved
# **************************************************************************
# * 本地实验脚本,支持多类目分类,非均衡类目
# * Command: bash run.sh
# * Command: 二分类模式, 开启 task_type="single", 同时确认对应日期目录下有single字符串的数据文件
# * Command: 多分类模式, 开启 task_type="multi",同时确认对应日期目录下有multi字符串的数据文件
# * @author wangqiwen
# * @date 2024/09/22 13:00
# **************************************************************************
# -------- 数据日期 --------
date_str="20240914"
home_dir="/mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/wangqiwen"
main_dir="${home_dir}/change_query"
# [prompt,label,history]
# -------- 任务类型 --------
# [index,session_id,lang,intent,label_id,label_name,context_num,prompt,context_info]
task_type="multi" # single(二分类), multi(多分类)
# task_type="single" # single(二分类)
# -------- 数据地址 --------
train_path="${main_dir}/data/output_format_${task_type}_train_cls_${date_str}.csv"
dev_path="${main_dir}/data/output_format_${task_type}_val_cls_${date_str}.csv"
test_path="${main_dir}/data/output_format_${task_type}_test_cls_${date_str}.csv"
# 多种数据格式
# [index,session_id,lang,intent,label_id,label_name,context_num,prompt,context_info]
# index,session_id,lang,label,context_num,prompt,context
# data_map='{"prompt":"prompt","label":"label_id", "history":"context_info"}'
data_map='{\"prompt\":\"prompt\",\"label\":\"label_id\", \"history\":\"context_info\"}'
train_path="${main_dir}/data/${date_str}/output_format_${task_type}_train_cls_${date_str}.csv"
dev_path="${main_dir}/data/${date_str}/output_format_${task_type}_val_cls_${date_str}.csv"
test_path="${main_dir}/data/${date_str}/output_format_${task_type}_test_cls_${date_str}.csv"
model_name="bert-base-multilingual-cased" # v100-32g
# model_name="bigbird-roberta-base" # a100-80g
# model_name="bigbird-roberta-large" # a100-80g OOM
model_path="${home_dir}/model/bert/${model_name}"
max_length=512
# max_length=2048
per_device_batch_size=64 # 128 单机越界
# per_device_batch_size=96
[ $task_type = "single" ]&&{
# 二分类
num_classes=2
class_list="0,1"
class_weight="1,1"
}||{
# 多标签
# num_classes=11
# class_list="2,3,4,10,20,30,41,42,51,52,53"
# class_weight="1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1"
# 新版
num_classes=6
class_list="0,10,20,30,40,50"
class_weight="1,1,1,1,1,1"
# cross_entropy
loss_type="cross_entropy"
# focal loss
# loss_type="focal_loss"
# cb loss
# loss_type="cb_loss"
# class_weight="17830,3240,1678,1372,224,6" # 各类目频次分布, 临时占用权重字段
}
cmd="""
python3 main.py
--per_device_batch_size $per_device_batch_size
--data_map \"$data_map\"
--train_path $train_path
--dev_path $dev_path
--test_path $test_path
--model_path $model_path
--max_length $max_length
--num_classes ${num_classes:-2}
--class_list "${class_list:-0,1}"
--class_weight "${class_weight:-1,1}"
--loss_type ${loss_type:-cross_entropy}
"""
echo "[Info] 开始执行命令: \n $cmd"
eval $cmd
train.py
入口程序: train.py
主要参数
- –
step1 2 3 - –
deployment-typesingle_gpu single_node multi_node 不同type主要是参数的设置不同 - –
actor-model: “1.3b”, “6.7b”, “13b”, “66b” 预训练模型,默认是1.3b的模型 - –
reward-model:使用的是 350m 的模型 - 其他参数参考train.py中的说明
配置脚本
配置脚本:
- training/step1_supervised_finetuning/training_scripts/single_node/
run_1.3b.sh
train.py 程序会调用 run_1.3b.sh 来执行模型训练
run_1.3b.sh中可以设置参数,并调用对应的 main.py 来开始模型训练
训练程序
训练程序:
training/step1_supervised_finetuning/main.py
核心训练脚本,主要功能如下:
- 数据/模型下载
- 模型训练
- 评价与测试用程序:
prompt_eval.py - 用于测试训练后的模型,并提供了微调前后的对比。
Step1:监督微调
使用指定数据微调预训练模型。
启动训练: 执行下面命令开启模型训练。
- 请先确保设置了 CUDA 并激活了 conda 运行环境
python3 train.py --step 1 --deployment-type single_gpu #单GPU训练
python3 train.py --step 1 --deployment-type single_node #多GPU训练
python3 train.py --step 1 --deployment-type multi_node #多Node训练
三种方式中
single_gpu只适合训练小模型- 而 single_node 和 multi_node 适合训练较大模型。
建议
- 第一次运行时,用
single_gpu,这种模式输出的错误信息会更详细。 - 如果遇到 GPU 内存不足的问题,尝试使用
single_node和multi_node来训练。 - 如果问题仍然存在,需要手动调整
batch-size。
此步骤主要进行:
- 模型下载:自动下载对应的模型
- 保存到
~/.cache/huggingface/hub/models--facebook--opt-1.3b
- 保存到
- 数据下载
Dahoas/rm-static# 对话(prompt,response,chosen,rejected)Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf# 对话(prompt,response,chosen,rejected)Dahoas/synthetic-instruct-gptj-pairwise# 对话(prompt,chosen,rejected)yitingxie/rlhf-reward-datasets# 对话(prompt,chosen,rejected)openai/webgpt_comparisons# 带人工打分的数据,comparisons with human feedback,19,578 comparisons)stanfordnlp/SHP# 18个领域的385k 人类标注数据
- 模型训练:模型训练完成之后会被存储在
output/actor-models/1.3b下面training.log文件来查看训练的进度。
评价与测试:
- 打开文件
run_prompt.sh添加 baseline 模型,和 finetune 后的模型:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
python prompt_eval.py \
--model_name_or_path_baseline facebook/opt-1.3b \
--model_name_or_path_finetune ../../output/actor-models/1.3b
评价程序会调用 prompt_eval.py 来分别输出 baseline 和 finetune 后模型的结果。
执行此代码,先切换到 step1_supervised_finetuning 目录下。
cd training/step1_supervised_finetuning
bash evaluation_scripts/run_prompt.sh
常见问题:
- 训练过程,无法找到GPU,或者GPU调用错误,可以尝试使用如下设置:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1# 2块GPUexport CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7# 8块GPU
- 训练过程,出现端口被占用的问题
- 设置 MASTER_ADDR 和 MASTER_PORT,尤其是多个node训练,要设置 MASTER_ADDR。
export MASTER_ADDR=127.0.0.1# 多node时,需要设置为主node的IP或者机器名export MASTER_PORT=29701- 以上设置,也可以在
run1.3b.sh文件中进行设置,例如:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 deepspeed --master_addr=127.0.0.1 --master_port=29701 main.py
- 评价过程出现模型参数不匹配问题:
model.decoder.embed_tokens.weight: found shape torch.Size([50272, 2048]) in the checkpoint and torch.Size([50265, 2048]) in the model ...- 原因: 模型被finetune后,Token对应的词典数量发生了变化,导致输入数据维度变化了(bug,输入端应尽量保持与预训练模型一致)。
- 打开文件
prompt_eval.py,增加新 config 读取脚本,并把来源模型从 baseline 模型中修改为finerune后的模型: config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path_finetune)# 新增model_fintuned = get_model(config, args.model_name_or_path_finetune, tokenizer)
- 评价过程,出现 RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory
- 当对大模型评价时,可能会碰到。比如在32G GPU上使用13b的模型。
- 建议尝试使用 chat.py 命令(需要移动到 DeepSpeed-Chat 目录下),执行方式如下:
python chat.py --path output/actor-models/1.3b
Step2:Reward模型微调
任务介绍:
- 第三步(Step3)中,强化学习阶段需要使用奖励模型。
- 奖励模型会对模型生成的答案进行打分,Step3 的强化训练会根据这些分数对模型进行优化,从而使最终模型生成更高分的答案。
- 奖励模型同样基于预训练模型进行训练,这里用 350M 的 opt 模型。
启动训练:
- 启动训练方法与前面类似:
python3 train.py --step 2 --deployment-type single_gpu #单GPU训练
python3 train.py --step 2 --deployment-type single_node #多GPU训练
python3 train.py --step 2 --deployment-type multi_node #多Node训练
训练数据:
- 单GPU训练时只使用了 Dahoas/rm-static 数据
- 多GPU训练使用了更多的数据:
- Dahoas/rm-static
- Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf
- Dahoas/synthetic-instruct-gptj-pairwise
- yitingxie/rlhf-reward-datasets
- openai/webgpt_comparisons
- stanfordnlp/SHP
评价与测试:
步骤:
- 打开文件 run_eval.sh 设置 –model_name_or_path 参数。
- 转移到目录 step2_reward_model_finetuning 下
- 执行:bash evaluation_scripts/run_eval.sh
常见错误:
- 与上面类似,出现GPU内存不足错误
- 调整batch-size或用更多GPU训练。
- 如:在 run_350m.sh 文件中添加参数
--per_device_train_batch_size 8将默认batch size从16修改为8,如果问题依然存在,可以进一步调小。
Step3:RLHF训练
任务介绍:
RLHF 是基于人类反馈的强化学习的缩写。根据官方介绍,此步训练面临两个主要挑战:
同时使用多个模型的内存消耗问题:此步训练不仅使用被训练的主模型,还使用奖励模型进行评分,因此会占用更多的 GPU 内存。 如何有效地生成答案:在 RLHF 训练过程中,需要生成多个备选答案。由于模型一次推理只能生成一个答案,因此需要进行多次模型推理,这种操作会大幅度增加训练时间。 在此实例中,通过将 DeepSpeed 训练和推理功能整合为一个统一的混合引擎(Hybrid Engine)来应对这些挑战。更多详细信息可以参考官方说明。
在此步骤首次运行时,会安装并编译新的工具(transformer_inference)。如果编辑过程出现问题,建议升级 PyTorch 和 CUDA 版本。在我的环境下,使用 PyTorch 2.0 和 CUDA 11.7 下可以成功编译。
启动训练:
python3 train.py --step 3 --deployment-type single_gpu #单GPU训练
python3 train.py --step 3 --deployment-type single_node #多GPU训练
python3 train.py --step 3 --deployment-type multi_node #多Node训练
此步训练后的模型被存储在 output/step3-models/1.3b/ 下。
常见问题:
Q/A 1. GPU内存不足时,在sh脚本中增加如下设置,调整batch size: –per_device_train_batch_size 8 –per_device_mini_train_batch_size=8 8 评价与测试 【观看视频解说】
使用 chat.py 命令(需要移动到 DeepSpeed-Chat 目录下)进行评价与测试。 执行方式如下:
python chat.py –path output/step3-models/1.3b/actor 上面的程序可以启动13b的模型,但是66b的模型无法成功运行。
DeepSpeed 用法
DeepSpeed 用法
- 【2023-5-19】huggingface DeepSpeed文档的笔记:DeepSpeed 入门教程
DeepSpeed 支持功能
- Optimizer state partitioning (ZeRO stage 1)
- Gradient partitioning (ZeRO stage 2)
- Parameter partitioning (ZeRO stage 3)
- Custom mixed precision training handling
- A range of fast CUDA-extension-based optimizers
- ZeRO-Offload to CPU and NVMe
ZeRO 汇总
一句话总结:
partitioning instead of replicating,划分而不是复制
DeepSpeed 的 ZeRO config文件可分为几类:优化器 → 梯度 → 参数 → offload
ZeRO Stage 1: 划分optimizer states。- 优化器参数被划分到多个memory上,每个momory 进程只负责更新自己那部分参数。
ZeRO Stage 2: 划分gradient。- 每个memory,只保留它分配到的optimizer state所对应的梯度。
- 这很合理,因为梯度和optimizer是紧密联系在一起的。只知道梯度,不知道optimizer state,是没有办法优化模型参数的。
ZeRO Stage 3: 划分模型参数,或不同的layer.- ZeRO-3会在forward和backward 时,自动将模型参数分配到多个memory。
由于ZeRO-1只分配optimizer states(参数量很小),实际使用时,一般只会考虑ZeRO-2和ZeRO-3。
ZeRO 级别:
| 级别 | 特点 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
Zero-0 |
不使用所有类型分片,仅使用DeepSpeed作为DDP | |
Zero-1 |
优化器状态 | 分割 Optimizer States, 减少4倍内存,通信容量和数据并行性相同 |
Zero-2 |
梯度 | 分割 Optimizer States和Gradients,减少8倍内存,通信容量和数据并行性相同 |
Zero-3 |
参数 | 分割 Optimizer States、gradients、Parameters,内存减少与数据并行度呈线性关系。例如,在64个GPU(Nd=64)之间进行拆分将产生64倍的内存缩减。通信量有50%的适度增长 |
Zero-Infinity |
参数+offload | Zero-Infinity是 Zero-3 扩展,通过使用 NVMe 固态硬盘扩展 GPU 和 CPU 内存来训练大型模型 |
Zero stage和offload
- 由于通信增加,故从左到右越来越慢
- Stage 0 (DDP) > Stage 1 > Stage 2 > Stage 2 + offload > Stage 3 > Stage 3 + offloads
- 由于去除各模块冗余和卸载数据到CPU,故从左到右,显存占用越来越少
- Stage 0 (DDP) < Stage 1 < Stage 2 < Stage 2 + offload < Stage 3 < Stage 3 + offloads
【2025-8-5】最新汇总对比
| 特性 | ZeRO-1 | ZeRO-2 | ZeRO-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 分片对象 | 优化器状态 | 优化器状态 + 梯度 | 参数 + 梯度 + 优化器状态 |
| 显存占用 | $N \times (P + G) + \frac{O}{N}$ | $N \times P + \frac{G + O}{N}$ | $\frac{P + G + O}{N}$ |
| 显存节省 | 中等 | 高 | 最高 |
| 通信开销 | 低(仅同步优化器状态) | 中等(同步梯度) | 高(同步参数、梯度) |
| 适用模型规模 | 中小型模型 | 中大型模型 | 超大规模模型 |
| 硬件要求 | 单机多 GPU 或低带宽集群 | 分布式集群 | 高带宽分布式集群 |
| 典型应用场景 | 优化器状态占显存主导 | 梯度和优化器状态占主导 | 参数占显存主导 |
# ======== 单卡 =========
# 单卡 使用方法
deepspeed --num_gpus=1 examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py ...
# 单卡,并指定对应的GPU
deepspeed --include localhost:1 examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py ...
# ======== 多卡 =========
# 多GPU 使用方法1
torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node=2 your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json
# 多GPU 使用方法2
deepspeed --num_gpus=2 your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json
# ======== 多机多卡 =========
# 多节点多卡 方法1:多个节点上手动启动
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node=8 --nnode=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=hostname1 --master_port=9901 your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json
# 多节点多卡 方法2:创建 hostfile 文件,只需在一个节点上启动
hostname1 slots=8
hostname2 slots=8
# 然后运行
deepspeed --num_gpus 8 --num_nodes 2 --hostfile hostfile --master_addr hostname1 --master_port=9901 your_program.py <normal cl args> --deepspeed ds_config.json
# 参数传递
TrainingArguments(..., deepspeed="/path/to/ds_config.json")
# or
ds_config_dict = dict(scheduler=scheduler_params, optimizer=optimizer_params)
TrainingArguments(..., deepspeed=ds_config_dict)
# 在SLURM上运行,略,参见原始文档
# 在jupyter中运行,略,参见原始文档
为什么单卡也能用deepspeed?
- 使用
ZeRO-offload,将部分数据 offload 到 CPU,降低对显存的需求 - 提供了对显存管理,减少显存碎片
ZeRO-0 配置
禁用所有分片,此时将DeepSpeed视为DDP使用 (stage默认值:0)
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 0
}
ZeRO-1 配置
ZeRO第一阶段的优化,将优化器状态进行切分
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 1
}
ZeRO-2 配置
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 2,
"allgather_partitions": true,
"allgather_bucket_size": 3e8,
"overlap_comm": true,
"reduce_scatter": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": 3e8,
"contiguous_gradients": true
}
- allgather_partitions: 在每个步骤结束时,从所有GPU中选择使用allgather集体操作或一系列广播集体操作之间的方式,以收集更新后的参数。 (默认值:true)
- allgather_bucket_size: 用于调节Allgather操作的分桶大小。将张量分成较小的桶有助于在通信过程中更高效地传输数据。较大的allgather_bucket_size值会导致每个桶的尺寸增大,可能加速通信操作,但也需要更多内存来存储中间结果。选择合适的桶大小需要根据实际情况进行调整。(默认值:5e8)
- overlap_comm: 控制通信与计算是否交叠执行。当设置为True时,DeepSpeed将尝试在梯度计算期间并行进行梯度通信。这有效地缩短通信时间,从而加速整个训练过程。(默认值:false)
- reduce_scatter: 使用reduce或reduce scatter来替代allreduce以平均梯度。(默认值:true)
- reduce_bucket_size: 用于控制Allreduce操作的分桶大小。将张量分为较小的桶有助于数据在通信过程中的更高效传输。随着reduce_bucket_size值的增大,每个桶的尺寸也随之增大,这或许能加速通信操作,但同时也需要更多内存来存储中间结果。合适的桶大小应根据实际情况进行适当调整。(默认值:5e8)
- contiguous_gradients: 在梯度产生时将其复制到一个连续的缓冲区中。在反向传播过程中避免了内存碎片化问题。(默认值:true)
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupLR",
"params": {
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 2,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"allgather_partitions": true,
"allgather_bucket_size": 2e8,
"overlap_comm": true,
"reduce_scatter": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": 2e8,
"contiguous_gradients": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false
}
说明
- overlap_comm:控制是否使用通信与计算的重叠。
- 当设置为True时,DeepSpeed将在梯度计算时尝试并行执行梯度通信。可以有效地减少通信时间,从而加速整个训练过程。
- allgather_bucket_size:用于控制Allgather操作的分桶大小。
- Allgather操作是指在分布式训练中,每个进程收集其他所有进程的张量,并将这些张量按顺序拼接起来。通过将张量划分为较小的桶(buckets),可以在通信过程中更高效地传输数据。
- allgather_bucket_size值越大,每个桶的大小越大,通信操作可能会变得更快,但也需要更多的内存来存储中间结果。合适的桶大小要根据实际情况调整。
- reduce_bucket_size:类似于allgather_bucket_size,用于控制Allreduce操作的分桶大小。
- Allreduce操作是将所有进程的某个张量进行规约(例如求和),并将结果广播回所有进程。通过将张量划分为较小的桶,可以更高效地传输数据。
- reduce_bucket_size值越大,每个桶的大小越大,通信操作可能会变得更快,但同时也需要更多的内存来存储中间结果。合适的桶大小需要根据实际情况进行调整。
- overlap_comm使用的是allgather_bucket_size和reduce_bucket_size值的4.5倍。
- 如果设置为5e8,需要9GB显存(5e8 x 2Bytes x 2 x 4.5)。
- 如果内存大小是8GB或更小,需要将这些参数减少到约2e8,从而避免OOM,这需要3.6GB显存。
- 如果在大容量GPU上也出现OOM,也需要做同样的调整。
- 在deepspeed==0.4.4中新增了 round_robin_gradients 选项,可以并行化CPU的offload。
- 当梯度累积的步数增加,或者GPU数量增加时,会有更好的性能优势。
ZeRO-3 配置
ZeRO-3
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"overlap_comm": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"sub_group_size": 1e9,
"reduce_bucket_size": 1e6,
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 4e6,
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 1e4,
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 1e9,
"stage3_max_reuse_distance": 1e9,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
},
- sub_group_size: 控制在优化器步骤中参数更新的粒度。参数被分组到大小为sub_group_size的桶中,每个桶依次进行一次更新。当与ZeRO-Infinity中的NVMe offload同时使用时,sub_group_size决定了在优化器步骤期间从NVMe迁移到CPU内存的模型状态的粒度。这有助于避免超大模型对CPU内存的过度占用。在不使用NVMe offload时,请保持其默认值。若遇到内存不足(OOM)情况,可以考虑减小sub_group_size。当优化器迭代较缓慢时,也可以考虑增大sub_group_size。(默认值:1e9)
- stage3_prefetch_bucket_size: 预取参数的固定缓冲区大小。较小的值使用的内存较少,但可能会因通信而增加停顿。(默认值:5e8)
- stage3_max_live_parameters: 保留在GPU上的完整参数数量的上限。(默认值:1e9)
- stage3_max_reuse_distance: 根据参数在未来何时再次使用的指标来决定是舍弃还是保留参数。如果一个参数在不久的将来会再次被使用(小于stage3_max_reuse_distance),则会保留该参数以减少通信开销。在遇到内存不足(OOM)的情况下,可以降低stage3_max_live_parameters和stage3_max_reuse_distance的值。(默认值:1e9)
- stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save: 在保存模型时启用模型FP16权重合并。对于大型模型和多GPU环境,这是一项在内存和速度方面代价较高的操作。(默认值:false)
ZeRO-3 中不使用 allgather_partitions、allgather_bucket_size 和 reduce_scatter 配置参数
(其他参数如grad_hooks、round_robin_gradients本文未提及)
配置示例
{
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "WarmupLR",
"params": {
"warmup_min_lr": "auto",
"warmup_max_lr": "auto",
"warmup_num_steps": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu",
"pin_memory": true
},
"overlap_comm": true,
"contiguous_gradients": true,
"sub_group_size": 1e9,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": "auto",
"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": "auto",
"stage3_max_live_parameters": 1e9,
"stage3_max_reuse_distance": 1e9,
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 2000,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false
}
说明
- stage3_max_live_parameters 保留在 GPU 上的完整参数数量的上限。
- stage3_max_reuse_distance 将来何时再次使用参数的指标,从而决定是丢弃参数还是保留参数。
- 如果一个参数在不久的将来要再次使用(小于 stage3_max_reuse_distance),可以保留以减少通信开销。 使用activation checkpointing时,这一点非常有用。
- 如果遇到 OOM,可以减少 stage3_max_live_parameters 和 stage3_max_reuse_distance。 除非正在使用activation checkpointing,否则它们对性能的影响应该很小。 1e9 会消耗 ~2GB。 内存由 stage3_max_live_parameters 和 stage3_max_reuse_distance 共享,所以不是相加的,一共 2GB。
- stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save 在保存模型时启用模型 fp16 权重合并。
- 对大型模型和多GPU,在内存和速度方面都是一项昂贵的操作。 如果打算恢复训练,目前需要使用它。 未来的更新将消除此限制。
- sub_group_size 控制在optimizer steps中更新参数的粒度。
- 参数被分组到 sub_group_size 的桶中,每个桶一次更新一个。
- 当与 ZeRO-Infinity 中的 NVMe offload一起使用时,sub_group_size 控制模型状态在optimizer steps期间从 NVMe 移入和移出 CPU 内存的粒度。 防止超大模型耗尽 CPU 内存。不使用NVMe offload时,使其保持默认值。出现OOM时,减小sub_group_size。当优化器迭代很慢时,可以增大sub_group_size 。
- ZeRO-3 中未使用 allgather_partitions、allgather_bucket_size 和 reduce_scatter 配置参数
ZeRO-stage-0
stage 0会禁用所有的分片,然后把DeepSpeed当作时DDP来使用。
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 0
}
}
ZeRO-stage-1
只对优化器参数进行分片,可以加速一丢丢
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 1
}
}
NVMe Support
- ZeRO-Infinity 需要使用 ZeRO-3
- ZeRO-3 会比 ZeRO-2 慢很多。使用以下策略,可以使得ZeRO-3 的速度更接近ZeRO-2
- 将stage3_param_persistence_threshold参数设置的很大,比如6 * hidden_size * hidden_size
- 将offload_params参数关闭(可以极大改善性能)
如何选择不同的Zero stage和offload
- 从左到右,越来越慢
- Stage 0 (DDP) > Stage 1 > Stage 2 > Stage 2 + offload > Stage 3 > Stage 3 + offloads
- 从左到右,所需GPU显存越来越少
- Stage 0 (DDP) < Stage 1 < Stage 2 < Stage 2 + offload < Stage 3 < Stage 3 + offloads
ZeRO Infinity
除 stage2 和 3 外,介绍下 ZeRO-Infinity。
ZeRO-Infinity 是stage-3 进阶版本,依赖 NVMe 支持。
- offload所有模型参数状态到CPU以及NVMe上。
- 得益于NMVe协议,除了使用CPU内存之外,ZeRO可以额外利用
SSD(固态),从而极大地节约了memory开销,加速了通信速度。
官网对于ZeRO-Infinity的详细介绍:
DeepSpeed官方教程 :
ZeRO-Infinity has all of the savings of ZeRO-Offload, plus is able to offload more the model weights and has more effective bandwidth utilization and overlapping of computation and communication.
HuggingFace官网:
It allows for training incredibly large models by extending GPU and CPU memory with NVMe memory. Thanks to smart partitioning and tiling algorithms each GPU needs to send and receive very small amounts of data during offloading so modern NVMe proved to be fit to allow for an even larger total memory pool available to your training process. ZeRO-Infinity requires ZeRO-3 enabled.
具体config文件,以及使用事项,请参见官网。
GPU上进行前向和后向计算,将梯度传给CPU,进行参数更新,再将更新后的参数传给GPU。
为了提高效率,将计算和通信并行起来
- GPU在反向传播阶段,待梯度值填满bucket后,一边计算新梯度,一边将bucket传输给CPU
- 当反向传播结束,CPU基本上已经有最新的梯度值了,同样,CPU在参数更新时也同步将已经计算好的参数传给GPU
四个计算类节点:FWD、BWD、Param update 和 float2half,前两个计算复杂度大致是 O(MB), B是batch size,后两个计算复杂度是 O(M)。
- 为了不降低计算效率,将前两个节点放在GPU,后两个节点不但计算量小还需要和Adam状态打交道,所以放在CPU上,Adam状态自然也放在内存中,为了简化数据图,将前两个节点融合成一个节点FWD-BWD Super Node,将后两个节点融合成一个节点Update Super Node。如下图右边所示,沿着gradient 16和parameter 16两条边切分。
调参步骤
将batch_size设置为1,通过梯度累积实现任意的有效batch_size
- 如果OOM则,设置–gradient_checkpointing 1 (HF Trainer),或者 model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
- 如果OOM则,尝试ZeRO stage 2
- 如果OOM则,尝试ZeRO stage 2 + offload_optimizer
- 如果OOM则,尝试ZeRO stage 3
- 如果OOM则,尝试offload_param到CPU
- 如果OOM则,尝试offload_optimizer到CPU
- 如果OOM则,尝试降低一些默认参数。比如使用generate时,减小beam search的搜索范围
- 如果OOM则,使用混合精度训练,在Ampere的GPU上使用bf16,在旧版本GPU上使用fp16
- 如果仍然OOM,则使用ZeRO-Infinity ,使用offload_param和offload_optimizer到NVME
- 一旦使用batch_size=1时,没有导致OOM,测量此时的有效吞吐量,然后尽可能增大batch_size
- 开始优化参数,可以关闭offload参数,或者降低ZeRO stage,然后调整batch_size,然后继续测量吞吐量,直到性能比较满意(调参可以增加66%的性能)
一些其他建议
- 如果训模型from scratch,hidden size最好可以被16整除
- batch size最好可以被2整除
优化器和调度器
当不使用offload_optimizer 时,可以按照下表,混合使用HF和DS的优化器和迭代器,除了HF Scheduler和DS Optimizer这一种情况。
| Combos | HF Scheduler | DS Scheduler |
|---|---|---|
| HF Optimizer | Yes | Yes |
| DS Optimizer | No | Yes |
优化器
- 启用 offload_optimizer 时可以使用非 DeepSpeed 的优化器,只要它同时具有 CPU 和 GPU 的实现(LAMB 除外)。
- DeepSpeed 的主要优化器是 Adam、AdamW、OneBitAdam 和 Lamb。 这些已通过 ZeRO 进行了彻底测试,建议使用。
- 如果没有在配置文件中配置优化器参数,Trainer 将自动将其设置为 AdamW,并将使用命令行参数的默认值:–learning_rate、–adam_beta1、–adam_beta2、 –adam_epsilon 和 –weight_decay。
- 与 AdamW 类似,可以配置其他官方支持的优化器。 请记住,它们可能具有不同的配置值。 例如 对于 Adam,需要将 weight_decay 设置为 0.01 左右。
- 此外,offload在与 Deepspeed 的 CPU Adam 优化器一起使用时效果最佳。 如果想对offload使用不同的优化器,deepspeed==0.8.3 以后的版本,还需要添加:
{
"zero_force_ds_cpu_optimizer": false
}
调度器
- DeepSpeed 支持 LRRangeTest、OneCycle、WarmupLR 和 WarmupDecayLR 学习率调度器。
- Transformers和DeepSpeed中调度器的overlap
- WarmupLR 使用 –lr_scheduler_type constant_with_warmup
- WarmupDecayLR 使用 –lr_scheduler_type linear
混合精度
由于 fp16 混合精度大大减少了内存需求,并可以实现更快的速度,因此只有此训练模式表现不佳时,才考虑不使用混合精度训练。
通常,当模型未在 fp16 混合精度中进行预训练时,会出现这种情况(例如,使用 bf16 预训练的模型)。 这样的模型可能会溢出,导致loss为NaN。 如果是这种情况,使用完整的 fp32 模式。
- 如果是基于 Ampere 架构的 GPU,pytorch 1.7 及更高版本将自动切换为使用更高效的 tf32 格式进行某些操作,但结果仍将采用 fp32。
- 使用 Trainer,可以使用
--tf32启用它,或使用--tf32 0或--no_tf32禁用它。
PyTorch 默认值是使用tf32。
自动混合精度
fp16- 可用
pytorch-likeAMP 方式或者apex-like方式 - 使用
--fp16--fp16_backend amp或--fp16_full_eval命令行参数时启用此模式
- 可用
bf16- 使用
--bf16or--bf16_full_eval命令行参数时启用此模式
- 使用
注意
- fp32/fp16 绝大多数硬件都支持,所以可用混合精度训练提高吞吐;
- 但 bf16/tf32 只有新的硬件才支持,V100/昇腾910等不支持
- bf16 具有和 fp32 相同的 range,但精度(也就是两个最小单位之间的间隔)降低
- bf16/fp32 进行混合精度训练,可以减少溢出几率
- 对于大型 transformer,bf16 损失的精度被证明不怎么影响收敛
- tf32 是 A100 中引入的新格式,用于替代 fp32,也即可以全程 tf32 训练或 bf16/tf32 混合训练
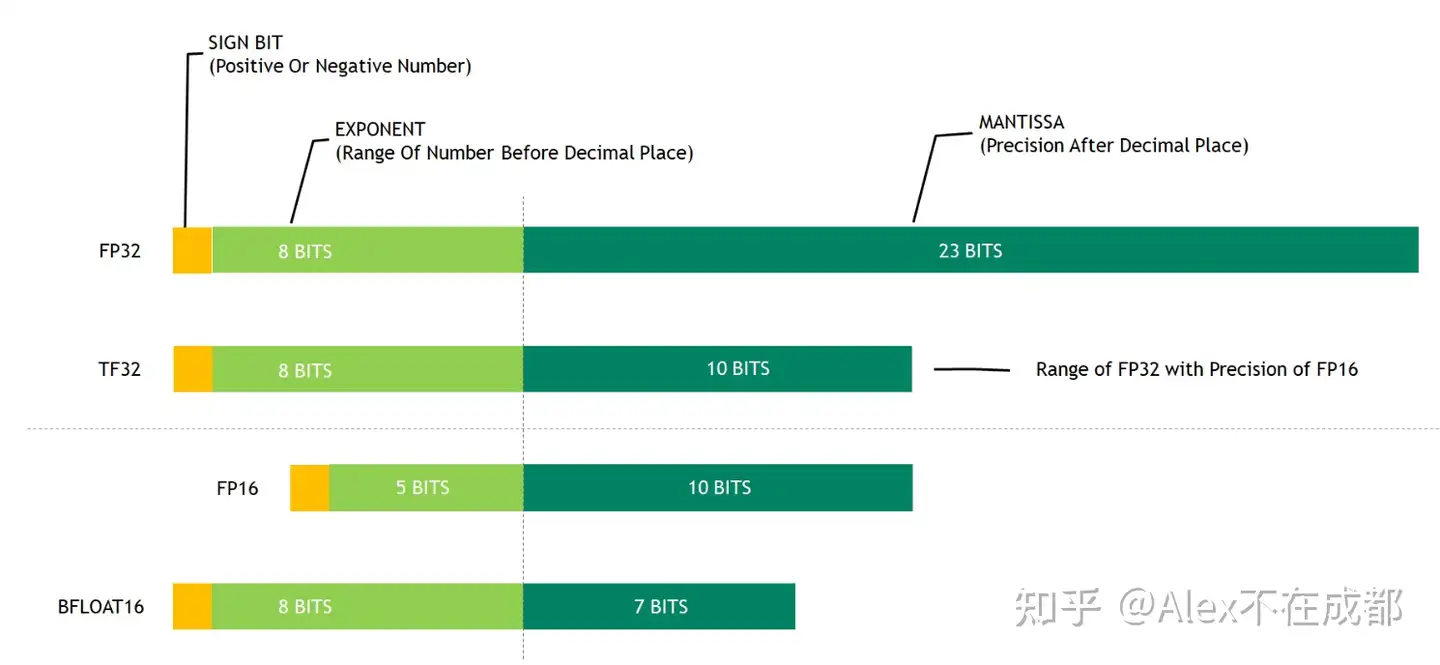
bf16/fp32 混合训练
- 因为两种格式在 range 对齐,并且 bf16 比 fp16 range 更大,所以比 fp16/fp32 混合训练稳定性更高。
- 但 fp16/fp32 混合训练 GPT-3 大模型也完全可行,只要解决可溢出问题
几个要点:
- fp32权重备份 + loss scaling 解决下溢出问题
- 对 loss 进行 scale:见左图
- 对 gradient 进行 scale:见右图
- 由于链式法则的存在,对梯度做直接做 scale 也是可以的,反而更划算。这样,所有前向后向都可以全用 fp16 (activation、weight、gradient 全用 fp16),只在进行更新的时候,才用 fp32 和 master weight 更新
- 跳过 NaN 的 batch
- dynamic loss scale (PyTorch 中采用的这种方案):在一个 window 内,如果没有 NaN,loss scale 变大(例如乘2);如果有 NaN,则降低 loss scale,并跳过 NaN 的 batch,不更新梯度
- 或将 INF 值改为 FP16 的最大值(需要实际验证)
- 基于 Tensorcore 进行矩阵乘加:在某些模型中,fp16 矩阵乘法的过程中,需要利用 fp32 来进行矩阵乘法中间结果的累加,以减少加法过程中的舍入误差,保证精度不损失
这也是为什么有些人说,只有 Volta 之后有 TensorCore 的 GPU (例如V100),才能利用 fp16+混合精度来进行加速。其他 GPU 如果硬要用 fp16,只能做 fp16 的 multiply-add operation,会有较大精度损失
NCCL
- 通讯会采用一种单独的数据类型
- 默认情况下,半精度训练使用
fp16作为reduction操作的默认值 - 可以增加一个小的开销并确保reduction将使用 fp32 作为累积数据类型
{
"communication_data_type": "fp32"
}
apex
- Apex 是一个在 PyTorch 深度学习框架下用于加速训练和提高性能的库。Apex 提供了混合精度训练、分布式训练和内存优化等功能,帮助用户提高训练速度、扩展训练规模以及优化 GPU 资源利用率。
- 使用–fp16、 –fp16_backend apex、 –fp16_opt_level 01 命令行参数时启用此模式
"amp": {
"enabled": "auto",
"opt_level": "auto"
}
混合精度训练
"fp16": {
"enabled": true,
"auto_cast": false,
"loss_scale": 0,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"hysteresis": 2,
"consecutive_hysteresis": false,
"min_loss_scale": 1
}
"bf16": {
"enabled": true
}
- auto_cast: 是否将输入强制转换为fp16数据类型 (默认值:false)
- loss_scale: 表示FP16训练的损失缩放值。默认值0.0启用动态损失缩放,否则该值将用于静态固定损失缩放 (默认值:0.0)
- initial_scale_power: 表示初始动态损失比例值的功率,实际损失规模计算为 (默认值:16)
- loss_scale_window: 代表动态损失缩放值上升/下降的窗口范围。(默认值:1000)
- hysteresis: 表示动态损耗缩放中的延迟偏移 (默认值:2)
- consecutive_hysteresis: 表示是否在达到不会溢出的迭代时重新填充滞后。(默认值:false)
- min_loss_scale: 表示最小动态损失比例值 (默认值:1)
注意:开启fp16后可能出现如上图所示overflow情况
- BF16: 配置以bfloat16浮点格式作为FP16的替代方式。
- bfloat16需要硬件支持, 例如,NVIDIA A100, 注意 v100不支持!。
- 使用bfloat16进行训练不需要损失缩放。(默认值:false)
获取模型参数
deepspeed会在优化器参数中存储模型的主参数,存储在global_step/optim_states.pt 文件中,数据类型为fp32。因此,想要从checkpoint中恢复训练,则保持默认即可
- 如果模型是在ZeRO-2模式下保存的,模型参数会以fp16的形式存储在pytorch_model.bin中
- 如果模型是在ZeRO-3模式下保存的,需要如下所示设置参数,否则pytorch_model.bin将不会被创建
{
"zero_optimization": {
"stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": true
}
}
- 在线fp32权重恢复(需要很多的RAM)略
- 离线获取fp32权重
python zero_to_fp32.py . pytorch_model.bin
ZeRO inference
只有ZeRO-3是有意义的,因为可以将参数分片:
deepspeed --num_gpus=2 your_program.py <normal cl args> --do_eval --deepspeed ds_config.json
估算需要的显存
- 可以通过下面的代码,先估算不同配置需要的显存数量,从而决定开始尝试的ZeRO stage。
python -c 'from transformers import AutoModel; \
from deepspeed.runtime.zero.stage3 import estimate_zero3_model_states_mem_needs_all_live; \
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B"); \
estimate_zero3_model_states_mem_needs_all_live(model, num_gpus_per_node=2, num_nodes=1)'
[...]
Estimated memory needed for params, optim states and gradients for a:
HW: Setup with 1 node, 2 GPUs per node.
SW: Model with 2783M total params, 65M largest layer params.
per CPU | per GPU | Options
70.00GB | 0.25GB | offload_param=cpu , offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=1
其它问题
- 启动时,进程被杀死,并且没有打印出traceback:CPU显存不够
- loss是NaN:训练时用的是bf16,使用时是fp16。常常发生于google在TPU上train的模型,如T5。此时需要使用fp32或者bf16。
多机多卡
【2024-3-25】DeepSpeed 多机多卡训练指南
配置:
- 7机14卡,每台服务器两张A800
- 问:为啥每台机只挂两张卡?
- 答:资源就这样,服务器是云厂商提供,都是PCIE连接,且单机最多只能挂四张卡。
服务器只允许内网访问,不能连接外网
因此,先搞定如何离线配置训练环境
离线配置训练环境
- 报错:conda was found to be deleted
- 解决:增加参数
--ignore-missing-files解决 如:conda pack -n 环境名 -o 新的环境名.tar.gz –ignore-missing-files
共享文件系统
多机多卡训练,配置个共享文件系统是有很多好处,比如
- 数据集和模型只需要存一份,更重要的是,在
- 模型保存时,将模型保存到共享文件系统下,就不用保存多份模型
- 如果没有共享文件系统,在每台服务器上都保存一份模型参数。
断点重训时,手动合并每台机器上的优化器参数,非常麻烦。
如果真的没有共享文件系统,那怎么办?
解决办法:
- 方式1、在deepspeed里配置checkpoint参数的use_node_local_storage
- 方式2、增加在TrainingArguments中配置参数–save_on_each_node即可
- 其实,huggingface中的deepspeed插件文档已经对没有共享文件系统的情况做了说明,确实比较难找,位置
"checkpoint": {
"use_node_local_storage": true
}
deepspeed stage2 配置样例:
{
"bfloat16": {
"enabled": false
},
"fp16": {
"enabled": "auto",
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"initial_scale_power": 16,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
},
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 2,
"allgather_partitions": true,
"allgather_bucket_size": 2e8,
"overlap_comm": true,
"reduce_scatter": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
"contiguous_gradients": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 1e5,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false,
"checkpoint": {
"use_node_local_storage": true
}
}
使用resume路径去恢复训练时,可能卡在:
- loading extention module …
GPU有占用,GPU利用率也有显示,此时,你应该检查你的device_map是否为auto,如果不是,那肯定会卡在这
如果device_map=”auto”,但代码还是卡在这,可能的解决办法:
多台服务器之间配置互相免密登录
- 必须要做的,最好在一开始就做好,能节省很多时间。
做法
- 每台服务器都安装 pdsh
多卡训练可能会碰到的问题
问题1:ninja已经安装,deepspeed 多机多卡
- RuntimeError: Ninja is required to load C++ extensions
答案1:在训练代码的开头加入:
/root/anaconda3/envs/baichuan/bin:是服务器的conda虚拟环境的bin目录
local_env = os.environ.copy() local_env[“PATH”]= “/root/anaconda3/envs/baichuan/bin:” + local_env[“PATH”] os.environ.update(local_env)
问题2:
- libcudart.so.12.2: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
答案2:
- 1、检查文件libcudart.so.12.2是否存在(正常来说都是存在的),不存在该文件的话,需要重装cuda
- 2、在命令行执行 sudo ldconfig /usr/local/cuda-12.2/lib64
执行训练的代码,每台机器上要有完全一致的一份,且存储的路径都要一致(包括软件的安装路径等)
问题
- 1: 模型初始化时,定义了
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config),后面没有调用。- 当使用 zero 3 时需要设置
dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config)。 - 具体说明请参考
- 当使用 zero 3 时需要设置
- 2: ZeRO 是什么?
ZeRO(Zero Redundancy Optimizer)是 DeepSpeed 一种优化技术,旨在提高大规模模型训练的效率和可扩展性。- 其中,
ZeRO Offload是ZeRO技术的一种变体,可以通过将模型参数存储在 CPU 上,从而减少模型训练时对GPU显存的占用,并加速模型参数的梯度累积、梯度压缩和通信等操作。 ZeRO 3 是在大模型进行模型参数并行时使用。
deepspeed 传参问题
deepspeed 传参问题总结
- 参数位置敏感: 尤其注意区分deepspeed参数和train.py参数
- 格式: deepspeed
ds参数train.pytrain参数
- 格式: deepspeed
- 别漏了 ds 开关
--deepspeed - ds_config.json: 放最后, 或
--deepspeed_config
alexnet 示例
踩过的一系列坑
deepspeed train.py -p 1 --steps=200 --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json --autotuning tune
# (1) autotuning 放 train.py 后面 → error: unrecognized arguments: --autotuning tune
# (2) train.py 挪至最后 → deepspeed: error: unrecognized arguments: -p
deepspeed -p 1 --steps=200 --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json --autotuning tune train.py
# (3) autotuning 放 train.py 后面 → AssertionError: DeepSpeed configuration is not provided
deepspeed --autotuning tune train.py -p 1 --steps=200 --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json
# (4) ds_config.json 放 --deepspeed 前面 → File ".../deepspeed/autotuning/autotuner.py", line 176, in _get_user_config if ".json" in user_args[idx + 1]: IndexError: list index out of range
# 加 deepspeed 参数
deepspeed --autotuning tune train.py -p 1 --steps=200 --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json --deepspeed
# 去掉冗余参数 --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json
deepspeed --autotuning tune train.py -p 1 --steps=200 --deepspeed --deepspeed_config=ds_config.json
# (5) 报错 没有 pdsh → apt-get install pdsh (失败) → 编译安装 pdsh, 设置prefix, 添加到 PATH
# ./configure –-with-ssh –-enable-static-modules –-prefix=/home/username && make && make install
# bashrc: export PATH=$PATH:/home/username/bin
# pdsh -V
# (6) 报错 → localhost: ssh: connect to host localhost port 22: Connection refused
ssh错误提交官方 issue
解法:ssh 服务异常, 启动ssh服务, 监听端口 22
# 测试, 复现成功
ssh root@127.0.0.1 -v
# OpenSSH_8.4p1 Debian-5+deb11u3, OpenSSL 1.1.1n 15 Mar 2022
# debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config
# debug1: /etc/ssh/ssh_config line 19: include /etc/ssh/ssh_config.d/*.conf matched no files
# debug1: /etc/ssh/ssh_config line 21: Applying options for *
# debug1: Connecting to 127.0.0.1 [127.0.0.1] port 22.
# debug1: connect to address 127.0.0.1 port 22: Connection refused
# ssh: connect to host 127.0.0.1 port 22: Connection refused
ps -ef | grep sshd # 查看结果中是否有sshd服务, 如果没有,安装ssh client,启动ssh
service sshd status # sshd is running.
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config # 开启 22 端口
/etc/init.d/ssh restart
# 测试
ssh root@127.0.0.1 -v
继续追查
- 官方有同样的错误: issue
# (7)
# [2024-04-20 19:30:23,366] [INFO] [scheduler.py:393:run_experiment] Done running exp_id = 0, exp_name = profile_model_info, with resource = localhost:0
# 100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:56<00:00, 56.53s/it]
# [2024-04-20 19:30:28,376] [ERROR] [autotuner.py:699:model_info_profile_run] The model is not runnable with DeepSpeed with error = unrecognized arguments: eyJ0cmFpbl9iYXRjaF9zaXplIjogMjU2LCAidHJhaW5fbWljcm9fYmF0Y2hfc2l6ZV9wZXJfZ3B1IjogMSwgIm9wdGltaXplciI6IHsidHlwZSI6ICJBZGFtIiwgInBhcmFtcyI6IHsibHIiOiAwLjAwMSwgImJldGFzIjogWzAuOSwgMC45OTldLCAiZXBzIjogMWUtMDh9fSwgInN0ZXBzX3Blcl9wcmludCI6IDEwLCAid2FsbF9jbG9ja19icmVha2Rvd24iOiBmYWxzZSwgIm5ub2RlIjogMSwgImF1dG90dW5pbmciOiB7ImVuYWJsZWQiOiB0cnVlLCAibW9kZWxfaW5mb19wYXRoIjogImF1dG90dW5pbmdfcmVzdWx0cy9wcm9maWxlX21vZGVsX2luZm8vbW9kZWxfaW5mby5qc29uIiwgIm1vZGVsX2luZm8iOiB7InByb2ZpbGUiOiB0cnVlfSwgIm1ldHJpY19wYXRoIjogImF1dG90dW5pbmdfcmVzdWx0cy9wcm9maWxlX21vZGVsX2luZm8vbWV0cmljcy5qc29uIn0sICJ6ZXJvX29wdGltaXphdGlvbiI6IHsic3RhZ2UiOiAzfSwgIm1lbW9yeV9icmVha19kb3duIjogZmFsc2V9 --per_device_train_batch_size 1
[2024-04-20 19:30:28,376] [INFO] [runner.py:366:run_autotuning] [End] Running autotuning
显存预估
DeepSpeed 使用难点在于时间和空间权衡。
- 分配更多参数到CPU上,虽然能够降低显存开销,但是也会极大地提升时间开销。
DeepSpeed 提供 memory估算代码:
from transformers import AutoModel
from deepspeed.runtime.zero.stage3 import estimate_zero3_model_states_mem_needs_all_live
## specify the model you want to train on your device
model_name_or_path = "/mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/yufeng/ModelHub/internlm2-1_8b"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=True)
## estimate the memory cost (both CPU and GPU)
estimate_zero3_model_states_mem_needs_all_live(model, num_gpus_per_node=1, num_nodes=1)
结果
- internlm2-1.8b 显存开销 32.37G, 实际开销翻倍(64G, batch_size,缓存)
- 使用 stage2和3后,显存开销被极大地降低,转而CPU内存消耗显著提升,模型训练时间开销也相应地增大。
Estimated memory needed for params, optim states and gradients for a:
HW: Setup with 1 node, 1 GPU per node.
SW: Model with 1889M total params, 189M largest layer params.
per CPU | per GPU | Options
47.50GB | 0.71GB | offload_param=cpu , offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=1
47.50GB | 0.71GB | offload_param=cpu , offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=0
42.22GB | 4.22GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=1
42.22GB | 4.22GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=cpu , zero_init=0
1.06GB | 32.37GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=none, zero_init=1
10.56GB | 32.37GB | offload_param=none, offload_optimizer=none, zero_init=0
启动任务前大概估计显存消耗,决定GPU数目,以及ZeRO-stage。
原则:
- 能直接多卡训练,就不用
ZeRO; - 能用
ZeRO-2就不用ZeRO-3.
无法识别 –local_rank=3
多GPU进行训练时, 错误信息
main.py: error: unrecognized arguments: --local_rank=3
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/opt/tiger/rh2/rh2/init/arnold.py", line 582, in main
raise Exception('failed to execute user script with exit code {}'.format(sub_exit_code))
Exception: failed to execute user script with exit code 2
原因: pytorch
- main.py 里的 ArgumentParser 未接收 local_rank 参数
解法: 添加local_rank参数
parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type=int, default=0)
pytorch 解法
python -m torch.distributed.launch已淘汰, 替换成torchrun
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 --master_port=27803 # replaced by
# 直接改成 torchrun
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 --master_port=27803 ...
CUDA out of memory
问题
torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 2.25 GiB.
GPU 0 has a total capacty of 79.35 GiB of which 210.19 MiB is free.
Process 1984273 has 79.14 GiB memory in use. Of the allocated memory 74.99 GiB is allocated by PyTorch, and 1.55 GiB is reserved by PyTorch but unallocated.
If reserved but unallocated memory is large try setting max_split_size_mb to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management and PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF
解法
run.sh
- 直接将 ds_config 文件添加到deepspeed后面, 或指定 deepspee_config 参数
DS_CONFIG_PATH="llm/ds_config.json"
deepspeed --master_port 30001 --autotuning tune \
./llm/training/conversation_reward/main.py \
--max_seq_len 3072 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 2 \
--weight_decay 0.1 \
--dropout 0.0 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 16 \
--zero_stage 2 \
--dtype bf16 \
--num_train_epochs 10 \
--train_data_path /mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/wangqiwen/session_process/data/train/cut_train_sequence_all_20240331.csv \
--val_data_path /mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/wangqiwen/session_process/data/test/cut_test_toNow_es_sequence_v2.csv \
--test_data_path /mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/wangqiwen/session_process/data/test/cut_test_toNow_en_sequence_v2.csv \
--model_name_or_path /mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/yufeng/ModelHub/internlm2-1_8b \
--output_dir /mnt/bn/flow-algo-cn/wangqiwen/model/checkpoints \
--save_steps 1000 \
--deepspeed $DS_CONFIG_PATH
# --deepspeed_config $DS_CONFIG_PATH
main.py
parser = deepspeed.add_config_arguments(parser) # 添加这行
args = parser.parse_args()
无法识别 –deepspeed
【2024-4-19】无法识别命令行参数 deepspeed, deepspeed_config
- 提官方issues
deepspeed 0.12.6
torch 2.1.0+cu121
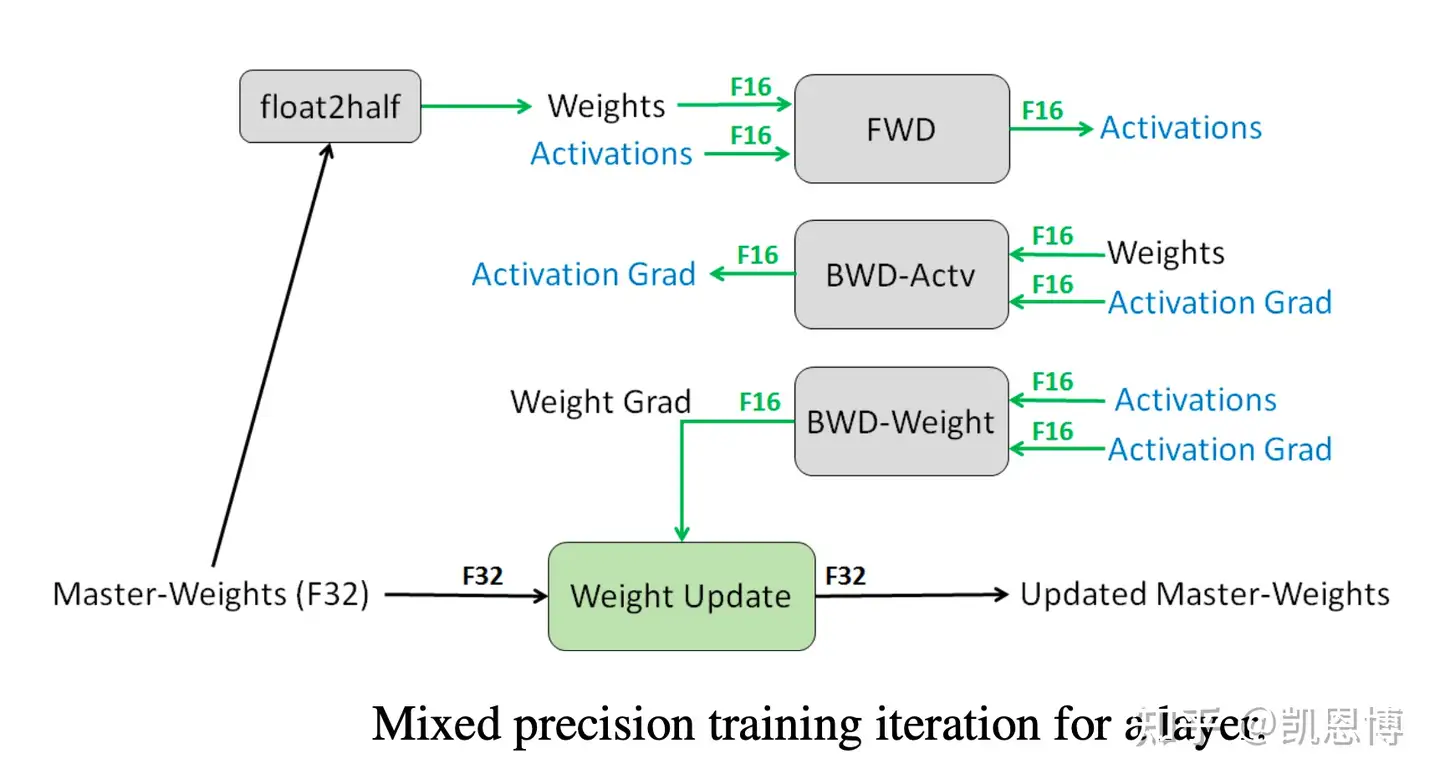
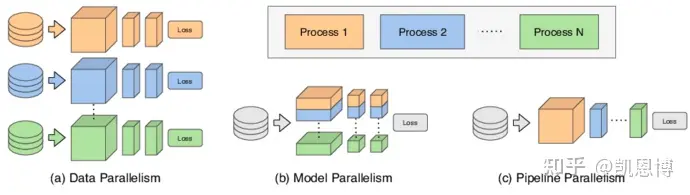
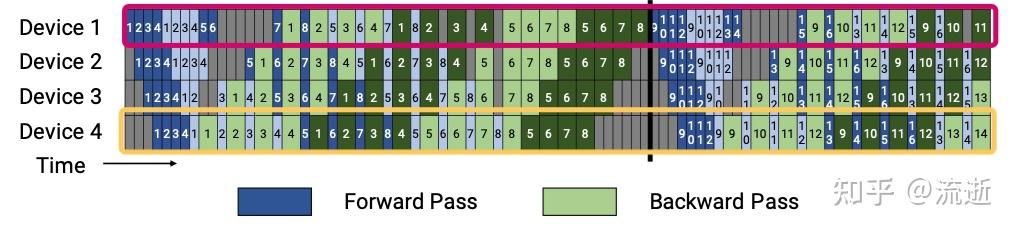
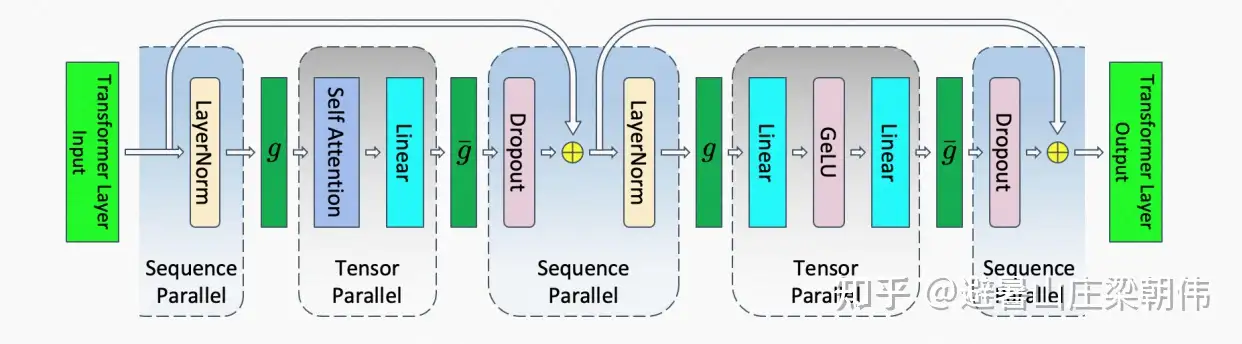
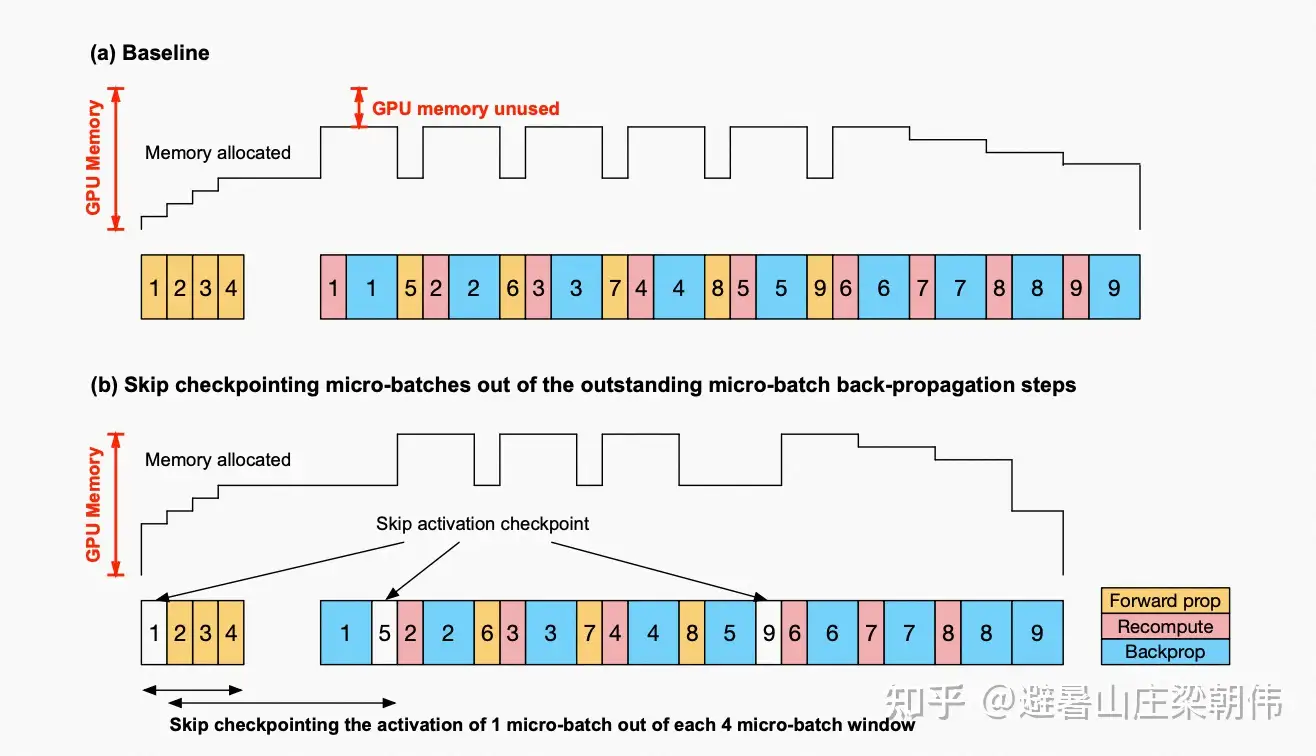
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏 
